| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 13, Number 3, June 2020, pages 96-100
Filling of Polyglycolic Acid Sheets for Closure of Gastrointestinal Fistulas With an Easily Deliverable Technique Using a Guidewire
Hideaki Kawabataa, b, Daiki Sonea, Katsutoshi Yamaguchia, Naonori Inouea, Yuji Okazakia, Yuki Uedaa, Misuzu Hitomia, Masatoshi Miyataa, Shigehiro Motoia
aDepartment of Gastroenterology, Kyoto Okamoto Memorial Hospital, Kyoto 613-0034, Japan
bCorresponding Author: Hideaki Kawabata, Department of Gastroenterology, Kyoto Okamoto Memorial Hospital, 100 Nishinokuchi, Sayama, Kumiyama-cho, Kuze-gun, Kyoto 613-0034, Japan
Manuscript submitted April 4, 2020, accepted April 29, 2020, published online June 18, 2020
Short title: Endoscopic Fistula Closure Using PGA Sheets
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/gr1284
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: This retrospective study aimed to investigate the suitable indications, methodology and long-term effect of the closure of gastrointestinal (GI) fistulas using polyglycolic acid (PGA) sheets and fibrin glue (FG) and to evaluate the usefulness of a delivery technique using a guidewire.
Methods: It involved 10 applications in six patients (median age 73 (range 53 - 78) years old, three men) with GI fistulas. A guidewire was introduced endoscopically or percutaneously into the fistula beyond the opposite orifice of the fistula with radiologic control. A tapered catheter was inserted over the guidewire, and the fistula was cleaned with an adequate quantity of saline. Subsequently, a small piece of PGA sheet was skewered onto the guidewire at the center and then pushed using the tapered catheter over the guidewire and delivered into the fistula. In cases of endoscopic procedure, the mucosa around the fistula was ablated, and the orifice of the fistula along with the surrounding mucosa was shielded with a piece of PGA sheet fixed with hemoclips and FG.
Results: Technical success of fistula closure was achieved in all applications, and no complications were observed after the procedure. The long-term occlusion of the fistula was ultimately achieved in four of six patients at 202 - 654 days (median duration, 244 days) after the last procedure with one or two applications.
Conclusions: The closure of GI fistulas using PGA sheets and FG demonstrated long-term efficacy for upper GI fistula of a certain length, and the filling technique using a guidewire ensured a safe smooth procedure.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal fistula; Polyglycolic acid sheet; Fibrin glue; Guidewire
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Gastrointestinal (GI) fistulas can develop as chronic processes of postoperative anastomotic leakage, inflammatory disease or malignancy, with a postoperative incidence of 0-35% [1-3]. Conservative management of fistulas based on parenteral nutrition and bowel rest, as well as on control of infection, electrolytic disturbances, and local care of the fistula tract, has been attempted; however, persistent fistulas that fail to close even after prolonged conservative treatment require surgical intervention, and even then patients can still develop a life-threatening condition [4].
Recently, a number of approaches for the endoscopic management of GI leaks and fistulas, including clip closure, endoscopic suturing, stent placement and tissue sealants, have been developed, and the efficacy of such procedures has been reported [1, 5]. As one endoscopic treatment with tissue sealants, endoscopic closure using polyglycolic acid (PGA) sheets with fibrin glue (FG) has been attempted due to the harmless nature of these sheets and the satisfactory results have been achieved in various surgical fields [6-12]. Nakano et al [13] evaluated the clinical efficacy of endoscopic plombage using PGA sheets and FG to close GI fistulas in 10 cases, and 70% of fistulas were successfully closed with one to four applications during the observation period (median duration 31 (range 0 - 60) months). In addition, concurrent additional techniques, including ablation with argon plasma coagulation (APC) and shielding of the orifice using a PGA sheet, were attempted to promote the fixation of filling PGA sheets [11-14]. However, various aspects, including suitable indications, methodology and the long-term effects of this procedure, have not been sufficiently investigated.
In previously reported cases using PGA sheets, the sheets were delivered with biopsy forceps and stuffed into the fistula using a tapered catheter or closed biopsy forceps [6-11, 13]. This procedure should be repeated several times in order to prevent mesh dislocation; however, it can be technically difficult to apply the sheets, and blindly inserting such pushing devices can injure the fistula. Therefore, we developed a technique to easily deliver PGA sheets with a guidewire and reported a case of GI fistula that was successfully treated with filling and shielding of PGA sheets and FG using this delivery technique [12].
The aim of this study was to investigate the suitable indication, methodology and long-term effects of the closure of GI fistulas using PGA sheets and FG and to evaluate the usefulness of our novel delivery technique using a guidewire.
| Materials and Methods | ▴Top |
We retrospectively reviewed the clinical data of all consecutive patients who received GI fistula closure using PGA sheets and FG in our institution between September 2017 and December 2019.
GI fistula was diagnosed and measured with contrast imaging performed by introducing contrast medium through the fistula. A guidewire (0.64 mm in diameter, RAYELISSE; CREATE MEDIC, Kanagawa, Japan) was introduced endoscopically or percutaneously into the fistula beyond the opposite orifice of the fistula with radiologic control. A tapered catheter was inserted over the guidewire, and the fistula was cleaned with an adequate quantity of saline. Subsequently, a small piece of a PGA sheet (Neoveil; Gunze Medical Division, Kyoto, Japan) was skewered onto the guidewire at the center and then pushed using the tapered catheter (MTW; MTW Endoskopie, Wesel, Germany) over the guidewire for delivery into the fistula. The size and number of PGA sheets for filling were determined according to the diameter and length of each fistula, respectively.
When an endoscopic procedure was performed, the mucosa around the fistula was ablated with APC, and then a piece of a PGA sheet was applied to the orifice of the fistula along with the surrounding mucosa and fixed with hemoclips (EZ Clip; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at the edge of the sheet. If this shielding procedure was not technically indicated, the orifice of the fistula was directly closed with hemoclips. When a percutaneous approach was used, the filled PGA sheets were fixed by inserting a soft catheter. Finally, 1 mL of FG (Beriplast P Combi-Set; CSL Behring Pharma, Tokyo, Japan) was sprayed over the entire sheet with an injection needle. The closure of the fistula was confirmed by contrast imaging and recurrence was diagnosed based on leakage from the cutaneous fistula or an increase in drainage.
This study followed the ethical guidelines for studies involving human subjects based on the Helsinki Declaration. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kyoto Okamoto Memorial Hospital.
| Results | ▴Top |
Six consecutive patients received GI fistula closure using PGA sheets and FG with a total of 10 applications. The patient characteristics are outlined in Supplementary Material 1 (www.gastrores.org). The study population included three men and three women with a median age of 73 (range 53 - 78) years old. Five cases developed as a postsurgical complication, and one case was caused by a perforated esophageal ulcer. Three, two, and one cases were anastomo-cutaneous, colono-cutaneous, and esophago-thoracic fistula, respectively. This procedure was attempted once or twice for each patient (10 applications in total). The median number of days from the onset to the procedure was 102 days (range 9 - 881). The median orifice diameter was 4.5 mm (range 1 - 6 mm), and the median length of the fistula was 37 mm (range 3 - 122). Fistula infection was found in five of six cases.
An endoscopic and percutaneous approach was selected in eight and two applications, respectively. The size of the filled PGA sheets was between 5 × 5 mm and 20 × 20 mm, whereas the median number of the filled PGA sheets was 3.5 (range 1 - 10). The median occluded length of the fistula was 16 mm (range 3 - 48 mm). After the endoscopic PGA-filling procedure, shielding with a PGA sheet following APC was applied in six applications, whereas hemoclips were added in two applications. In contrast, no concurrent procedure was performed in one application due to technical difficulties.
Technical success of fistula closure was achieved in all applications, and no complications were observed after the procedure. Representative images of the procedure (case 3) are shown in Figure 1. The long-term occlusion of the fistula was ultimately achieved in four of six patients 202 - 654 days (median duration, 244 days) after the last procedure, although the fistulas in three of four successfully treated cases were recanalized once 2 - 230 days (median duration, 9 days) after the first application, and the procedure then had to be repeated. Two cases who experienced recanalization several months after the first procedure (cases 1 and 2) had symptoms of infection, including a fever, redness, and pus drainage.
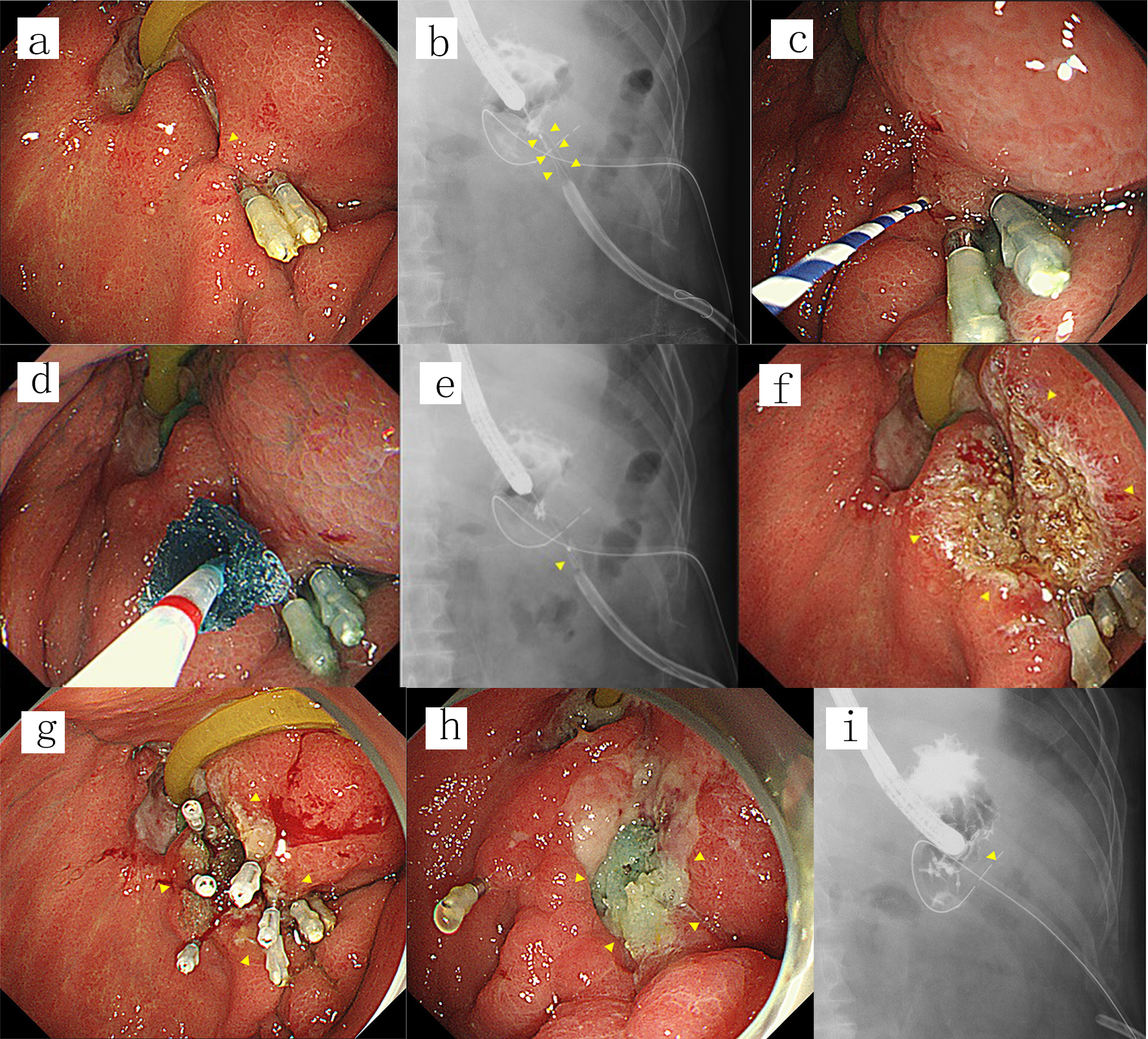 Click for large image | Figure 1. (a) A fistula was endoscopically detected at a gastrojejunal anastomosis (arrowhead) after failed fistula closure using hemoclips. (b, c) Contrast imaging performed by introducing contrast medium through the orifice of the fistula revealed an anastomo-cutaneous fistula (arrowheads). A guidewire was then introduced into the fistula (arrowhead). (d, e) A small piece of PGA sheet was skewered onto the guidewire at the center and then pushed using the tapered catheter over the guidewire and delivered into the fistula (arrowhead). This procedure was repeated five times while adjusting the depth of the PGA sheets on a radiogram. (f) The orifice of the fistula along with the surrounding mucosa was ablated using argon plasma coagulation (arrowheads). (g) The orifice of the fistula along with the surrounding mucosa was shielded by a piece of PGA sheet fixed with five hemoclips and fibrin glue (arrowheads). (h, i) The fistula was not detectable either endoscopically or on contrast radiograms by adding one more application 7 days after the first procedure (arrowheads), and the fistula remained closed until the patient died 465 days after the last procedure. PGA: polyglycolic acid. |
Two cases of colono-cutaneous fistula failed to close: one had been conservatively treated until death due to a worsening of the primary disease while no tumor was found to be associated with the fistula (case 4), and in another case the fistula was accompanied by an abscess cavity with early recanalization and therefore the patient underwent surgical treatment without any additional applications due to problems associated with local infectious control (case 6).
| Discussion | ▴Top |
The present study highlighted two important clinical points. First, we showed that the closure of GI fistulas using PGA sheets and FG was a safe, low-invasive treatment with long-term efficacy. Second, the filling technique using a guidewire ensured a safe, smooth procedure.
First, we showed that the endoscopic or percutaneous closure of GI fistulas with filling using PGA sheets and FG was a safe, low-invasive treatment with long-term efficacy. The technical success rate was 100% without any complications, and long-term complete fistula closure was achieved in two-thirds of the patients after ≤ 2 applications. In a previous retrospective study of 10 subjects, 70% of GI fistulas were successfully closed with endoscopic plombage using PGA sheets and FG with one to four applications [13], whose success rate was comparable with our present study. However, our cases required fewer applications than those in the previous study. Thorough washing and cleaning in the fistula before filling PGA sheets can prevent intra-fistula infection, which seemed to be related to late recanalization after this procedure. Accompanying ablation to the epithelialized mucosa using APC may induce the inflammation essential for wound repair and regeneration [15], which enhances the proliferation of granulation tissue with foothold of PGA sheets. Furthermore, the shielding procedure with the PGA sheet can prevent the dislocation or discharge of the filled PGA sheets due to peristaltic pressure or the continuous flow of digestive fluid. While endoclips were successfully used to gather the mucosa around the fistula after filling the fistula with PGA sheets [7, 13], such a procedure carries a risk of inducing incomplete closure. Recently, more powerful closure devices, such as the over-the-scope-clipping system and the endoscopic suturing technology, have been developed and demonstrated the availability for GI fistula closure in spite of concerns, including the technical difficulty, cost and long-term outcomes [16-20]. Such alternative techniques in combination with filling PGA sheets can help improve the long-term outcomes if these devices come to be easily and generally used in terms of technique and cost.
Regarding the indication for fistula closure using PGA sheets based on the results of the resent study, two conditions in which this technique was not feasible became clear: colonic fistula and fistulas with a short distance. Bacterial infection of the fistulas and PGA sheets is unavoidable even with thorough cleaning and washing before the procedure, as colonic fistulas are continuously exposed to enteric bacteria. Furthermore, adequate space in the fistulas is required for sufficient filling with PGA sheets. Nakano et al [13] suggested that epithelization of fistulas can lead to the insecure attachment of PGA sheets of fistulas and result in insufficient fistula closure. However, long-term fistula closure can be achieved even in an epithelized fistula through combination techniques, such as the ablation and shielding of the orifice, which promote attachment of the sheets.
Second, the filling technique using a guidewire ensured a safe smooth procedure. We can easily adjust the filling position based on radiograms and fill even deep sites of a fistula with the sheets. Furthermore, we can deliver several sheets simultaneously and adjust the size of the sheets depending on the size of the fistula. The sheets can be delivered in a retrograde fashion, from downstream of the fistula, such as via a percutaneous approach. Although careful guidance using a soft guidewire based on contrast imaging of the fistula is required in order to avoid fistula injury, moderate mechanical stimulation to the epithelized fistula due to guidewire movement might promote the formation of granulation tissue after filling with PGA sheets. To our knowledge, this is the first report clarifying the utility of a guidewire for a filling procedure with PGA sheets.
The present study is associated with several limitations. First, it was a retrospective single-center study with a small population. Larger, prospective, and multicenter studies are needed to confirm the utility of this procedure. Second, combination techniques, such as the ablation and shielding with PGA sheets, that may affect the outcomes were not indicated in all cases. A homogenized procedure including such techniques can enhance the rates of long-time fistula closure.
In conclusion, the closure of GI fistulas using PGA sheets and FG had long-term efficacy for upper GI fistulas of a certain length, and the filling technique using a guidewire ensured a safe, smooth procedure. Larger, prospective, and multicenter studies with a homogenized technique are needed to confirm the utility of this procedure.
| Supplementary Material | ▴Top |
Suppl 1. Characteristics of Patients, Details of the Procedure and Outcomes.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Author Contributions
HK, DS, KY, NI, YO, YU, MH, and MM contributed to endoscopic diagnosis and treatment. MM and SM supervised the findings of this work. HK wrote the manuscript with support from MH and SM. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Data Availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Rogalski P, Daniluk J, Baniukiewicz A, Wroblewski E, Dabrowski A. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(37):10542-10552.
doi pubmed - Falconi M, Pederzoli P. The relevance of gastrointestinal fistulae in clinical practice: a review. Gut. 2001;49(Suppl 4):iv2-10.
doi pubmed - Vakalopoulos KA, Daams F, Wu Z, Timmermans L, Jeekel JJ, Kleinrensink GJ, van der Ham A, et al. Tissue adhesives in gastrointestinal anastomosis: a systematic review. J Surg Res. 2013;180(2):290-300.
doi pubmed - Gonzalez-Pinto I, Gonzalez EM. Optimising the treatment of upper gastrointestinal fistulae. Gut. 2001;49(Suppl 4):iv22-31.
doi pubmed - Willingham FF, Buscaglia JM. Endoscopic Management of Gastrointestinal Leaks and Fistulae. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(10):1714-1721.
doi pubmed - Boudi FH, Lothe RA, Taggart RT. Human pepsinogen A (PGA): an informative gene complex located at 11q13. Hum Genet. 1990;84(3):293-295.
doi pubmed - Nagami Y, Shiba M, Tominaga K, Yamazoe S, Amano R, Fujiwara Y, Arakawa T. Endoscopic closure of gastrocutaneous leakage with polyglycolic acid sheets. Endoscopy. 2015;47(Suppl 1 UCTN):E455-456.
doi pubmed - Takano Y, Yamamura E, Kuroki Y, Maruoka N, Nagahama M, Takahashi H. Novel endoscopic treatment for colocutaneous fistula after severe acute pancreatitis: filling with a polyglycolic acid sheet. Endoscopy. 2015;47(Suppl 1 UCTN):E424-425.
doi pubmed - Tsujii Y, Kato M, Shinzaki S, Takigawa A, Hayashi Y, Nishida T, Iijima H, et al. Polyglycolic acid sheets for repair of refractory esophageal fistula. Endoscopy. 2015;47(Suppl 1 UCTN):E39-40.
doi pubmed - Yamamoto S, Endo S, Minegishi K, Shibano T, Nakano T, Tetsuka K. Polyglycolic acid mesh occlusion for postoperative bronchopleural fistula. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2015;23(8):931-936.
doi pubmed - Takimoto K, Hagiwara A. Filling and shielding for postoperative gastric perforations of endoscopic submucosal dissection using polyglycolic acid sheets and fibrin glue. Endosc Int Open. 2016;4(6):E661-664.
doi pubmed - Kawabata H, Okazaki Y, Inoue N, Kawakatsu Y, Hitomi M, Miyata M, Motoi S. Endoscopic closure of an anastomo-cutaneous fistula: Filling and shielding using polyglycolic acid sheets and fibrin glue with easily deliverable technique. Endosc Int Open. 2018;6(8):E994-E997.
doi pubmed - Nakano Y, Takao T, Morita Y, Sakaguchi H, Tanaka S, Ishida T, Toyonaga T, et al. Endoscopic plombage with polyglycolic acid sheets and fibrin glue for gastrointestinal fistulas. Surg Endosc. 2019;33(6):1795-1801.
doi pubmed - Kinoshita S, Nishizawa T, Hisamatsu T, Kanai T, Yahagi N. Polyglycolic acid sheet for closure of esophagobronchial fistula in a patient with Behcet's disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(5):1094-1096.
doi pubmed - Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, Longaker MT. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321.
doi pubmed - Cho J, Sahakian AB. Endoscopic closure of gastrointestinal fistulae and leaks. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2018;28(2):233-249.
doi pubmed - Monkemuller K, Peter S, Toshniwal J, Popa D, Zabielski M, Stahl RD, Ramesh J, et al. Multipurpose use of the 'bear claw' (over-the-scope-clip system) to treat endoluminal gastrointestinal disorders. Dig Endosc. 2014;26(3):350-357.
doi pubmed - Law R, Wong Kee Song LM, Irani S, Baron TH. Immediate technical and delayed clinical outcome of fistula closure using an over-the-scope clip device. Surg Endosc. 2015;29(7):1781-1786.
doi pubmed - Kobara H, Mori H, Fujihara S, Nishiyama N, Chiyo T, Yamada T, Fujiwara M, et al. Outcomes of gastrointestinal defect closure with an over-the-scope clip system in a multicenter experience: An analysis of a successful suction method. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(9):1645-1656.
doi pubmed - Callahan ZM, Su B, Kuchta K, Conaty E, Novak S, Linn J, Murad FM, et al. Endoscopic suturing results in high technical and clinical success rates for a variety of gastrointestinal pathologies. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020;24(2):278-287.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Gastroenterology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


