| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 6, December 2017, pages 352-358
Acute Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Characteristics and Clinical Outcome of Patients Treated With an Intensive Protocol
Georgia Diamantopouloua, Christos Konstantakisa, Anastasia Kottorοub, Georgios Skroubisc, Georgios Theocharisa, Vasileios Theopistosa, Christos Triantosa, Vasiliki Nikolopouloua, Konstantinos Thomopoulosa, d
aDepartment of Gastroenterology, University Hospital of Patras, 26504 Rio, Greece
bLaboratory of Molecular Oncology, University Hospital of Patras, 26504 Rio, Greece
cDepartment of Surgery, University Hospital of Patras, 26504 Rio, Greece
dCorresponding Author: Konstantinos Thomopoulos, Department of Gastroenterology, University Hospital of Patras, 26504 Rio, Greece
Manuscript submitted September 28, 2017, accepted October 11, 2017
Short title: ALGIB: Characteristics and Clinical Outcome
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/gr914w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: In recent years major advances have been made in the management of patients with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. The aim of this study was to investigate the characteristics and clinical outcome of patients with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (ALGIB) treated with an intensive protocol.
Methods: We analyzed the medical records of 528 patients with ALGIB. All patients after hemodynamic stabilization underwent colonoscopy during the first 24 h of hospitalization and capsule enteroscopy when needed. Patients with massive ongoing bleeding underwent computed tomography angiography (CTA), and when active bleeding was detected embolization was immediately performed.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 70.2 ± 14.6 years and 271 (51.3%) of them were men. At least one comorbidity was present in 464 patients (87.9%), cardiovascular disease in 266 (50.4%), while 158 (30%) patients were on antiplatelet drugs and 96 (18.2%) on anticoagulants. The most common causes of bleeding were diverticulosis (19.7%) and ischemic colitis (19.3%). Thirty-six patients (6.9%) had small intestinal bleeding. In 117 patients (22.2%) active bleeding or recent bleeding stigmata were found and in 82 of them (92.1%) endoscopic hemostasis was applied. Embolization was performed in 10 (1.9%) and was successful in seven (70%) cases, while surgical hemostasis was required in only six (1.1%) cases. Forty-four (8.3%) patients had a rebleeding episode, and 13 patients died with an overall mortality of 2.5%.
Conclusions: Management of ALGIB based on an intensive protocol is safe and effective. The bleeding source can be identified in most cases with a favorable outcome.
Keywords: Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding; Colonoscopy; Endoscopic therapy; Capsule endoscopy; Outcome
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (ALGIB), defined as bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract distal to the ligament of Treitz is a relatively common emergency. ALGIB can be further classified depending on the location of bleeding as small or large bowel. The clinical manifestations of ALGIB differ and depend on the rate, quantity and location of bleeding. Clinical presentations vary from bright red stools to dark blood with clots or even melena. ALGIB is often self-limited and resolves spontaneously in the majority of patients with no adverse outcome, while therapeutic intervention is needed in less than one-third of patients [1-3]. In contrast to upper gastrointestinal bleeding, it carries a lower recurrence and mortality rate [4-6].
The incidence of ALGIB is approximately 20 - 30 cases per 100,000 individuals and is probably rising due to the aging of the population, the higher rates of comorbidities and the increasing use of aspirin, anticoagulants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [7, 8].
Given that there is no specific treatment, the management of ALGIB is still based on intravascular volume resuscitation, hemodynamic stabilization and close monitoring of the patients. Diagnosis of the bleeding cause is sometimes difficult especially in the small bowel and non-surgical hemostasis is not always enough [9, 10]. In the last two decades, major advances have been made in both diagnostic and therapeutic methods in patients with ALGIB (computed tomography angiography (CTA), video capsule enteroscopy, enteroscopy, embolization, and endoscopic hemostasis). The aim of this study was to investigate the current characteristics of ALGIB and the clinical outcome of patients treated with an intensive diagnostic and therapeutic protocol.
| Materials and Methods | ▴Top |
Ethical considerations
This retrospective study was conducted in the Department of Gastroenterology of the University Hospital of Patras in Greece and was approved by the Scientific Committee on Research and Ethics of the Hospital.
Patients
All cases of ALGIB treated in our tertiary referral center from January 2010 to December 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. We included all patients older than 17 years admitted to our hospital for ALGIB or bled while inpatients for another reason. Patients presented with: 1) acute hematochezia, from bright red to marrow blood with clots or 2) melena with normal upper endoscopy and absence of blood in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. Patients with acute hematochezia or melena with documented lesion in the upper gastrointestinal tract and patients with chronic blood loss and/or iron deficiency anemia were excluded from the study.
All patients in our hospital were treated with an intensive diagnostic and therapeutic protocol. Clinical evaluation, resuscitation and appropriate replacement of blood loss were the main steps in the management of the patients. Endoscopy of large bowel was performed during the first 24 h of admission after colon preparation in the majority of patients. In cases of hemodynamic instability, emergent CTA was performed with embolization when appropriate. Patients with melena had gastroscopy for exclusion of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. When small bowel bleeding was suspected, capsule endoscopy was carried and rarely other type of enteroscopy.
Therapeutic endoscopic intervention included: injection hemostasis with adrenaline diluted at 1:10,000 in saline 0.9% in patients with active bleeding or stigmata of recent bleeding, the use of endoclips especially in post-polypectomy cases and the application of thermal contact treatment, such as argon plasma coagulation (APC) in patients with vascular ectasias.
Data collection
Data were collected retrospectively by identifying consecutive patients from both electronic and paper medical records registered in an electronic database. Demographic and clinical characteristics of all patients were recorded. Patient’s age, gender, clinical presentation of bleeding such as hematochezia, melena or dark blood with red clots, recent use of anticoagulant, antiplatelet or NSAIDs, the laboratory tests on admission (hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count, urea, and creatinine), the in-hospital presentation of bleeding, the comorbidities, the history of gastrointestinal bleeding, the history of gastrointestinal surgery (any kind of operation of gastrointestinal tract), the presence of active bleeding, the therapeutic intervention (endoscopic, embolization or surgery) and the outcome (days of hospitalization, need for blood transfusion, death, and bleeding relapse) were registered.
We analyzed the diagnostic procedures that were performed, the causes of bleeding and the localization of bleeding based on endoscopic (colonoscopy, capsule endoscopy, push enteroscopy, and intraoperative enteroscopy) and radiological (CTA and labeled red blood cells scintigraphy) findings. Diverticula were considered the cause of bleeding when active bleeding or stigmata of recent bleeding were observed or according to clinical presentation and course in the presence of diverticula and absence of other cause of bleeding. Ischemic colitis was diagnosed based on the findings of colonoscopy, pathology and clinical course.
Lastly, the clinical outcome was analyzed according to the duration of hospitalization, the number of transfused blood units per patient, the rate of rebleeding, the need for emergency surgical hemostasis and the mortality, defined as death within the hospitalization period. Blood transfusions were given to achieve a hemoglobin level of 9 mg/dL in non-cirrhotic or 8 mg/dL in cirrhotic patients.
Statistical analysis
Numerical data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation if the distribution was normal or median with range if not, and categorical data as frequencies. All variables were tested for normal distribution using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. In univariate analysis, categorical variables were tested using the Chi-square and Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables with and without normal distribution were compared using Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test, respectively. Clinical, biochemical and endoscopic factors that might have contributed to the mortality and rebleeding were evaluated. Multivariate analysis was performed using binary logistic regression analysis. The IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 21.0 (Armonk, NY: IBM Corp) was used for statistical analysis.
| Results | ▴Top |
A total of 528 cases of ALGIB were identified during the 7-year period. There was a slight predominance of male patients (51.3%) with a median age of 70.2 years (17 - 101). Most of them presented with hematochezia (84.7%), 73 (13.8%) cases had melena with red clots and a minority had melena (1.5%). Only 12 patients (2.3%) bled while hospitalized for other reason. Forty-one patients (7.8%) had gastrointestinal surgery history, 464 (87.9%) coexisting diseases and half patients had cardiovascular disease (50.4%). Thirty percent of all patients were under platelet aggregation-inhibitor drugs (clopidogrel, ticagrelor, prasugrel, and acetylsalicylic acid) and 18.2% were under anticoagulant agents (acenocoumarol, dabigatran, apixaban, rivaroxaban, classic heparin, and low molecular weight heparin) (Table 1).
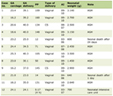 Click to view | Table 1. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Patients With ALGIB |
Lower gastrointestinal endoscopy following bowel preparation was performed in a total of 509 patients (96.4%) for diagnostic and therapeutic reasons. Additional procedures were performed: gastroscopy (n = 111, 21%), abdominal emergency CTA (n = 46, 8.7%) (of whom 10 (21.7%) underwent radiological embolization), capsule enteroscopy (n = 41, 7.8%), push enteroscopy (n = 10, 1.9%), intraoperative enteroscopy (n = 1, 0.2%) and scintigraphy with radio-labeled red cells (n = 2, 0.4%) (Table 2).
 Click to view | Table 2. Diagnostic Tools in Patients With ALGIB |
In 27 patients with ALGIB no cause of bleeding was identified despite thorough examinations, as needed. A diagnosis was established in 501 patients (94.9%). In 88% the bleeding site was in the large bowel while in 6.9% in the small bowel (Table 3).
 Click to view | Table 3. Localization of Bleeding and Diagnostic Examinations |
The most frequent causes of bleeding of large bowel were: diverticulosis (19.7%), ischemic colitis (19.3%), post-polypectomy bleeding (8.3%), hemorrhoids (8.1%), malignancy (8%), polyps (5.3%), and vascular ectasias (5.1%). The most frequent causes of bleeding of small bowel were vascular ectasias (2.1%) while in a proportion of 1.9% of patients appeared blood only in enteroscopy without determination of lesion (Table 4).
 Click to view | Table 4. Etiology of Bleeding in the Small and Large Bowel |
One hundred sixty-two patients (31.8%) had blood in colonoscopy (fresh red blood or dark blood or melena). Active bleeding was found in only 117 patients (22.2%) and 98 of them underwent a therapeutic intervention. Eighty-two patients underwent endoscopic intervention (15.6%): seven (1.3%) injection hemostasis with adrenaline solution, 16 (3%) hemostatic endoclips, 31 (5.8%) APC, 25 (4.7%) combination of injection hemostasis and endoclips, two (0.4%) combination of injection adrenaline and APC and one (0.2%) polypectomy. Ten patients required radiological embolization (1.9%) but only six patients required urgent surgery (1.1%) (Table 5).
 Click to view | Table 5. Clinical Outcome of Patients With ALGIB |
The mean hospitalization days were 4.3 (range 1 - 20). A total of 158 patients (30%) required blood transfusion with a mean of 0.9 (± 1.9) units (range 0 - 14) (Table 5). Thirteen patients died with an overall mortality of 2.5%. In univariate analysis mortality was associated with in-hospital presentation of bleeding (P = 0.032), small bowel localization of bleeding (P = 0.008), use of radiological embolization (P = 0.001), cirrhosis (P = 0.023) and active bleeding (P = 0.046) (Table 6). In multivariate analysis, mortality was associated with in-hospital presentation of bleeding (P = 0.021).
 Click to view | Table 6. Factors Associated With Death in Patients With ALGIB |
Bleeding recurred in 44 patients (8.3%). Ten patients had an in-hospital episode of rebleeding while 25 patients recurred in a period of 6 months after the first episode. In univariate analysis recurrence of bleeding was associated with male sex (P = 0.027), active bleeding (P = 0.004), presence of blood at colonoscopy (P = 0.025) and use of anticoagulants (P = 0.007). Also patients with ischemic colitis were less likely to rebleed (P = 0.047) whereas vascular ectasias were not significantly associated with recurrence (P = 0.064) (Table 7). In multivariate analysis, recurrence was associated with active bleeding on endoscopy (P < 0.001) and use of anticoagulants (P = 0.024).
 Click to view | Table 7. Factors Associated With Recurrence of Bleeding in Patients With ALGIB |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
ALGIB remains a relatively frequent cause of hospitalization worldwide, particularly in the elderly and it accounts for approximately one-third of all cases of acute gastrointestinal bleeding [8, 11]. The incidence of ALGIB is increasing in recent years in contrast to the incidence of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding [2, 4, 6, 7].
Diverticular bleeding remains the most frequent cause of bleeding in our study (19.7%) but in a lower percentage compared to previous reports (23%) [3, 4, 6, 7, 11]. Presence of colonic diverticula is very common in the population group suffering from ALGIB. Their co-existence with other causes of bleeding can make the differential diagnosis of ALGIB challenging. More advanced diagnostic methods such as capsule endoscopy and high definition colonoscopy together with better bowel preparation early in the post-bleeding phase improves diagnostic accuracy. The majority of ALGIBs resolves spontaneously with conservative medical treatment and thus a lesion may remain undiagnosed until bleeding recurrence or other symptomatology in the future [11, 12].
Ischemic colitis (IC) in our study is the second most common cause (19.3%) followed by post-polypectomy bleeding (8.3%). IC is a disease that affects more often women and patients on anticoagulant treatment [13]. It is the most common form of ischemic injury to the gastrointestinal tract and is usually self-limited with low morbidity [14]. Multiple medical conditions, as well as several pharmacological agents have been associated with IC [14]. IC and post-polypectomy bleeding are increasing in frequency and their increased rates are associated with the aging of the population, the high rates of comorbidities and the frequent anti-platelet/anticoagulant use in the peri-polypectomy period [4, 13]. The mean age of our patients with ALGIB was 70.2 years, 87.9% had at least one comorbidity, 50.4% had cardiovascular disease and almost 52.4% received some kind of antithrombotic therapy (antiplatelet agents, anticoagulant agents or NSAIDS). These therapies may cause bleeding lesions or may also cause a latent lesion to bleed acutely. This explains the high rate of polyps and colorectal cancers as causes of ALGIB (5.3% and 8% in our study) which, in the absence of anticoagulative therapy, cause chronic iron deficiency anemia and not acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding.
Hemodynamic resuscitation, risk stratification and management of antithrombotic agents remain the main steps in the management of patients with ALGIB [9]. However endoscopic hemostasis and/or arterial embolization might control bleeding and prevent rebleeding. Although it is debatable, early colonoscopy following adequate colon cleansing seems to be beneficial for patients with ALGIB and can be easily and safely performed during the first 24 h of patient presentation after hemodynamic stabilization. Adequate colon cleansing facilitates endoscopic visualization and diagnosis and may reduce the risk of bowel perforation [9]. Early colonoscopy for patients with ALGIB is safe, makes endoscopic therapy feasible as it identifies the bleeding source and reduces hospital stay [15]. In a previous study, Jensen et al found that early colonoscopy combined with endoscopic therapy reduced the duration of hospitalization, the risk of recurrence and the need for surgery compared with a control group [16].
Colorectal lesions responsible for bleeding were found in 88% of all patients. Endoscopic hemostasis was performed in 15.6% of whom 76.3% achieved permanent hemostasis in a long-term follow-up. Similar results have been presented in previous studies [9, 17]. Surgical hemostasis is rarely performed today in patients with ALGIB. In our study, only 1.1% of patients had emergency surgical hemostasis compared to rates up to 14% reported in previous studies [10, 18]. Moreover, currently emergency surgery is eclectic involving only the bleeding site and blind segmental colectomies are generally avoided. Intra-operative enteroscopy was rarely performed in our cohort reflecting the efficacy of an intensive diagnostic protocol to identify the site and nature of bleeding pre-operatively. The diagnostic accuracy of colonoscopy is higher compared to other diagnostic modalities such as angiography or nuclear scintigraphy (70-86% vs. 40-50%) [19, 20]. However, in massive ongoing bleeding not responding to resuscitation where colonoscopy is impossible, CTA may identify the bleeding source [19, 21-23]. CTA is feasible and correctly depicts the presence and location of active bleeding in most cases but has the limitation of decreased ability to detect the source in no actively bleeding patients [11, 21]. In our study, almost 9% had CTA; only 1.9% of patients underwent embolization with a success rate of 70%.
In literature, small bowel bleeding represents 2-9% of ALGIB [11] as in our study (6.9%). Video capsule endoscopy (VCE) is useful in patients with small bowel bleeding whose origin cannot be identified with conventional endoscopic or radiologic examinations [24]. Capsule endoscopy (CE) was highly diagnostic in our group. It is highly acceptable that the sooner CE is performed, the higher the diagnostic value. CE within 2 days of the last overt gastrointestinal bleeding after negative bidirectional endoscopic findings could improve the management of these patients providing a more rapid, appropriate and cost-effective therapeutic plan [25]. CE was better than CTA in a previous study [26].
Mortality rates ranging between 2% and 10% in ALGIB have been previously reported [2, 3, 7, 17]. In our study, mortality was low and associated with active bleeding, small bowel location and in-hospital presentation. Death in patients with ALGIB was not due to bleeding itself but due to coexisting diseases. Patients with severe co-morbidity cannot tolerate rapid blood loss.
In conclusion, management of patients with ALGIB according to an intensive diagnostic and therapeutic protocol is feasible, safe and effective. Identification of the bleeding source can be made in the majority of patients independently of the location (small or large intestine). Despite of the increased age and the frequent presence of concomitant diseases, mortality is low and the need for surgical treatment is relatively rare in patients with ALGIB.
Abbreviations
ALGIB: acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding; NSAIDs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CTA: computed tomography angiography; APC: argon plasma coagulation; VCE: video capsule endoscopy; CE: capsule endoscopy
| References | ▴Top |
- Bai Y, Peng J, Gao J, Zou DW, Li ZS. Epidemiology of lower gastrointestinal bleeding in China: single-center series and systematic analysis of Chinese literature with 53,951 patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(4):678-682.
doi pubmed - Arroja B, Cremers I, Ramos R, Cardoso C, Rego AC, Caldeira A, Eliseu L, et al. Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding management in Portugal: a multicentric prospective 1-year survey. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23(4):317-322.
doi pubmed - Hreinsson JP, Gumundsson S, Kalaitzakis E, Bjornsson ES. Lower gastrointestinal bleeding: incidence, etiology, and outcomes in a population-based setting. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25(1):37-43.
doi pubmed - Ghassemi KA, Jensen DM. Lower GI bleeding: epidemiology and management. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2013;15(7):333.
doi pubmed - Strate LL, Ayanian JZ, Kotler G, Syngal S. Risk factors for mortality in lower intestinal bleeding. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6(9):1004-1010; quiz 1955.
- Aoki T, Nagata N, Niikura R, Shimbo T, Tanaka S, Sekine K, Kishida Y, et al. Recurrence and mortality among patients hospitalized for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(3):488-494 e481.
- Longstreth GF. Epidemiology and outcome of patients hospitalized with acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(3):419-424.
pubmed - Lanas A, Garcia-Rodriguez LA, Polo-Tomas M, Ponce M, Alonso-Abreu I, Perez-Aisa MA, Perez-Gisbert J, et al. Time trends and impact of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation in clinical practice. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(7):1633-1641.
doi pubmed - Strate LL, Gralnek IM. ACG clinical guideline: management of patients with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(5):755.
doi pubmed - Moss AJ, Tuffaha H, Malik A. Lower GI bleeding: a review of current management, controversies and advances. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016;31(2):175-188.
doi pubmed - Marion Y, Lebreton G, Le Pennec V, Hourna E, Viennot S, Alves A. The management of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. J Visc Surg. 2014;151(3):191-201.
doi pubmed - Cirocchi R, Grassi V, Cavaliere D, Renzi C, Tabola R, Poli G, Avenia S, et al. New trends in acute management of colonic diverticular bleeding: a systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(44):e1710.
doi pubmed - Chavalitdhamrong D, Jensen DM, Kovacs TO, Jutabha R, Dulai G, Ohning G, Machicado GA. Ischemic colitis as a cause of severe hematochezia: risk factors and outcomes compared with other colon diagnoses. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74(4):852-857.
doi pubmed - Lewis JH. The risk of ischaemic colitis in irritable bowel syndrome patients treated with serotonergic therapies. Drug Saf. 2011;34(7):545-565.
doi pubmed - Nagata N, Niikura R, Sakurai T, Shimbo T, Aoki T, Moriyasu S, Sekine K, et al. Safety and effectiveness of early colonoscopy in management of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding on the basis of propensity score matching analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(4):558-564.
doi pubmed - Jensen DM, Machicado GA, Jutabha R, Kovacs TO. Urgent colonoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of severe diverticular hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(2):78-82.
doi pubmed - Farrell JJ, Friedman LS. Review article: the management of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21(11):1281-1298.
doi pubmed - Rios A, Montoya MJ, Rodriguez JM, Serrano A, Molina J, Ramirez P, Parrilla P. Severe acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding: risk factors for morbidity and mortality. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2007;392(2):165-171.
doi pubmed - Andrei GN, Popa B, Gulie L, Diaconescu BI, Martian BV, Bejenaru M, Beuran M. Highlighted steps of the management algorithm in acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding - case reports and literature review. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2016;111(1):74-79.
- Jensen DM, Machicado GA. Colonoscopy for diagnosis and treatment of severe lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Routine outcomes and cost analysis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997;7(3):477-498.
pubmed - Marti M, Artigas JM, Garzon G, Alvarez-Sala R, Soto JA. Acute lower intestinal bleeding: feasibility and diagnostic performance of CT angiography. Radiology. 2012;262(1):109-116.
doi pubmed - Chong V, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Accurate triage of lower gastrointestinal bleed (LGIB) - A cohort study. Int J Surg. 2016;25:19-23.
doi pubmed - Zahid A, Young CJ. Making decisions using radiology in lower GI hemorrhage. Int J Surg. 2016;31:100-103.
doi pubmed - Bresci G, Parisi G, Bertoni M, Tumino E, Capria A. The role of video capsule endoscopy for evaluating obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: usefulness of early use. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40(3):256-259.
doi pubmed - Kim SH, Keum B, Chun HJ, Yoo IK, Lee JM, Lee JS, Nam SJ, et al. Efficacy and implications of a 48-h cutoff for video capsule endoscopy application in overt obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Endosc Int Open. 2015;3(4):E334-338.
doi pubmed - Limsrivilai J, Srisajjakul S, Pongprasobchai S, Leelakusolvong S, Tanwandee T. A prospective blinded comparison of video capsule endoscopy versus computed tomography enterography in potential small bowel bleeding: clinical utility of computed tomography enterography. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51(7):611-618.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Gastroenterology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


