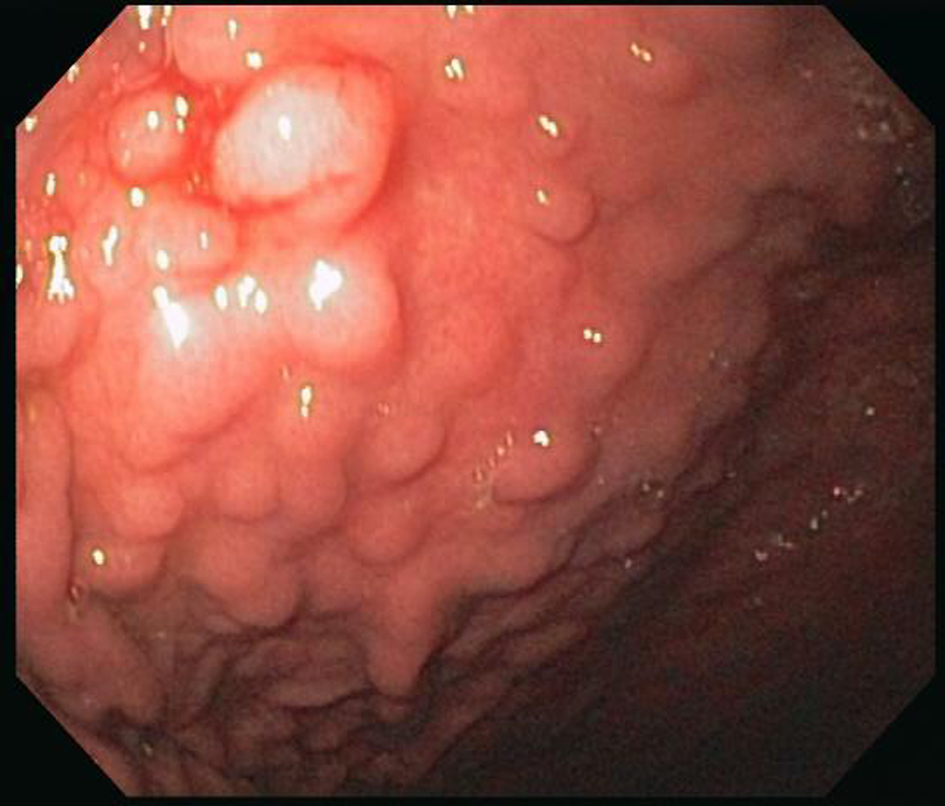
Figure 1. Endoscopy. There is a nodular appearing gastric mucosa prominent in the gastric body and antrum. These nodules are well demarcated.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 6, Number 4, August 2013, pages 139-144
Collagenous Gastritis a Rare Disorder in Search of a Disease
Figures

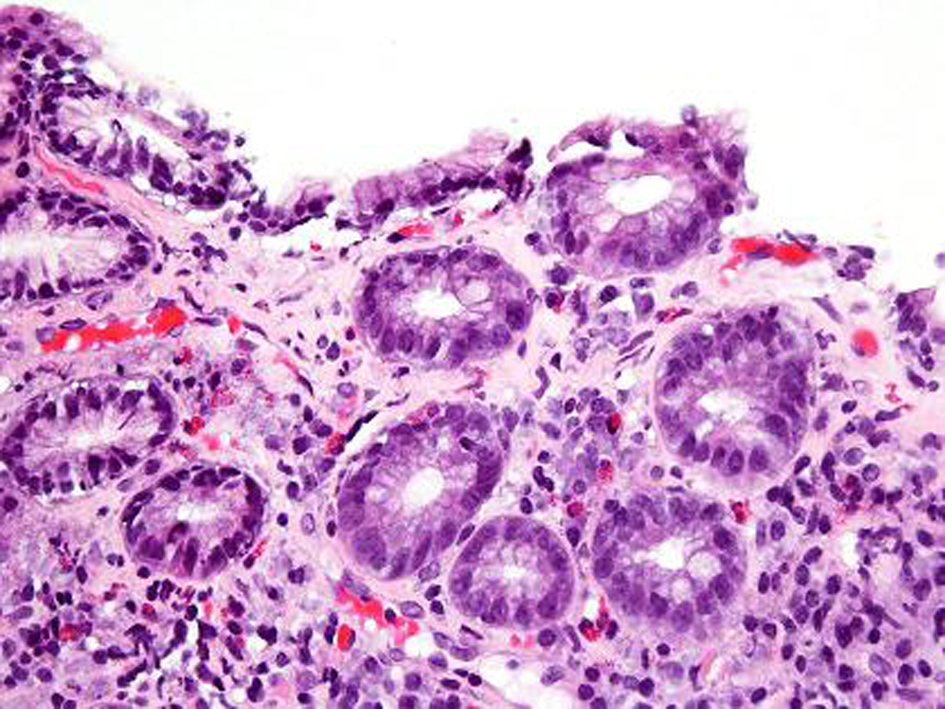
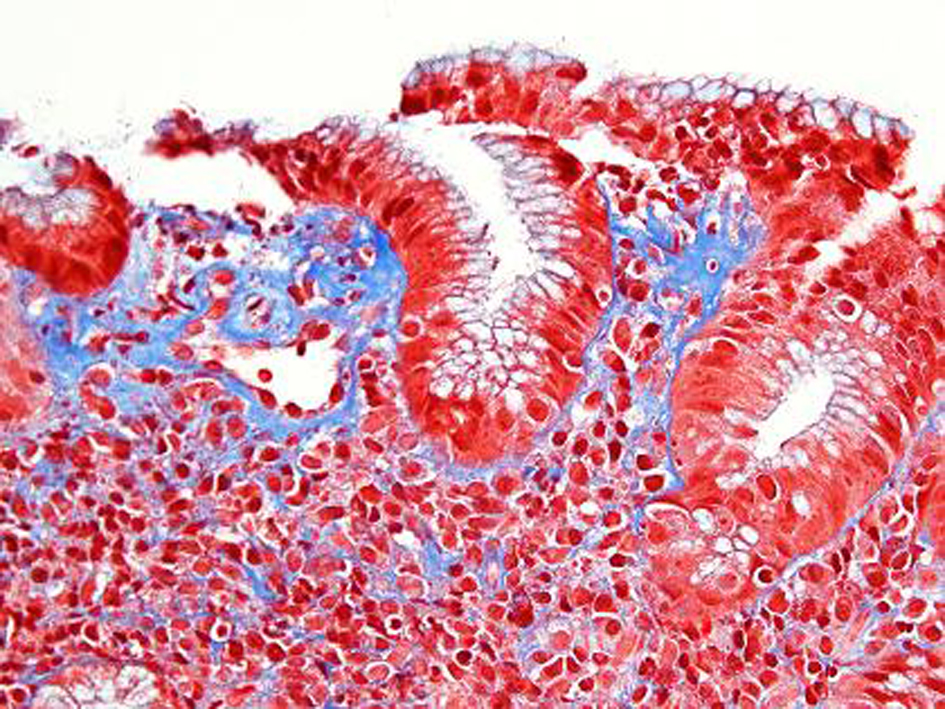
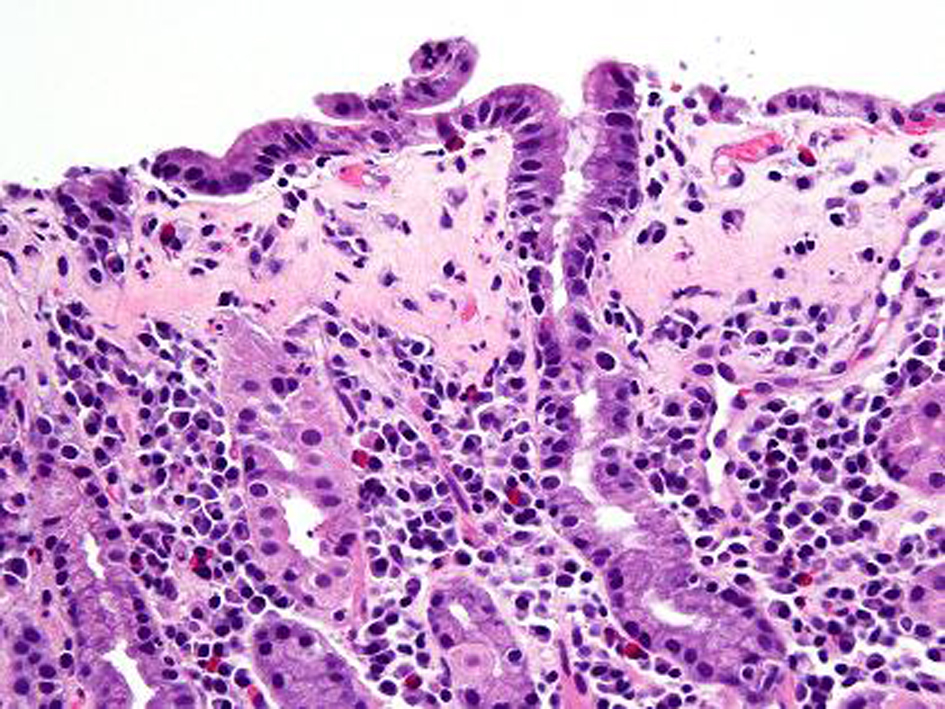
Table
| Collagenous Colitis | Collagenous Sprue | Collagenous Gastritis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Involvement | Colon | Small Intestine, mainly proximal | Stomach |
| First Described | 1976 by Windstorm | 1970 by Winestein | 1989 by Colleti and Trainer |
| Gender Prevelance | Female: Male 20:1 | Female > Male 2:1 | Not many cases to comment on gender prevelance |
| Age Prevelance | > 40 years, Peak in 6th and 7th decades | 40 - 80 years | Children and Adults |
| Most common symptoms | Watery non bloody diarrhea | Chronic diarrhea due to malabsorption, Weight loss | Abdominal pain, anemia in children Chronic watery diarrhea, irritable bowel symptoms in adults |
| Associated Drugs | NSAIDS, SSRI, Ranitidine. Possibly Aspirin, Acarbose, ticlopinine, PPI | ||
| Autoimmune diseases association | Celiac disease, thyroiditis, collagenous gastritis, collagenous colitis | Celiac disease, collagenous gastritis, collagenous colitis | Isolated in most children Adult form associated with collagenous colitis, lymphocytic gastritis, celiac disease and other autoimmune diseases |
| Colonoscopy findings | Mostly normal appearance to mucosal edema or hyperemia in some | Non specific: loss of mucosal folds, scalloping, mucosal erythema, mosaicism | Normal mucosa, diffuse gastric erythema, erosions, gastric hemorrhages, nodular mucosa |
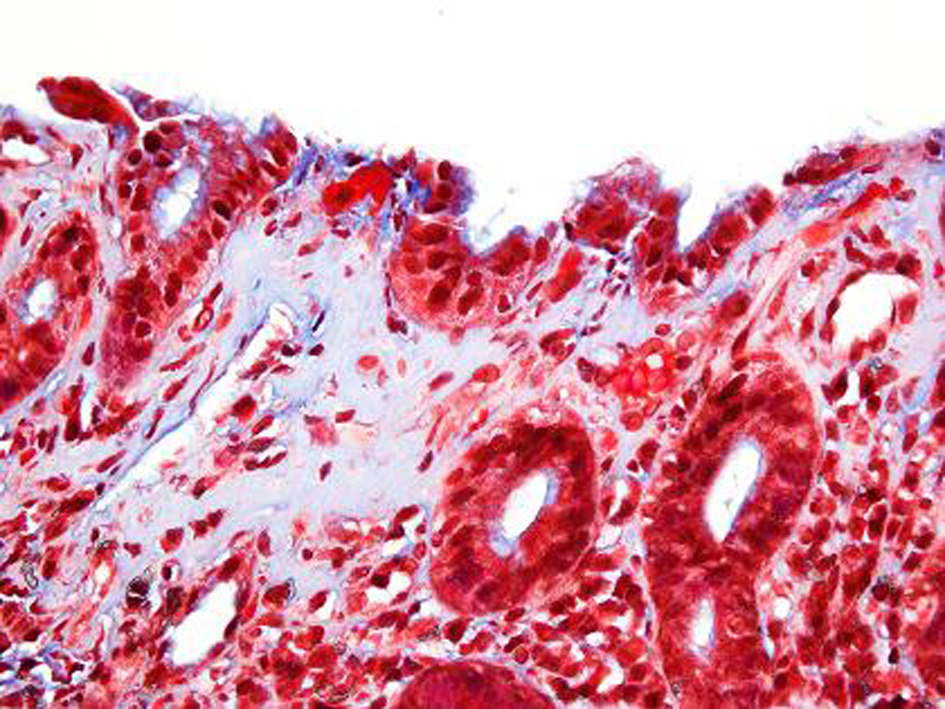
| Biopsy findings | Chronic inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells, lymphocytes and eosinophils in lamina propria with thickened subepithelial collagen bands ( > 10 mm) | Villous atrophy, crypt atrophy, chronic inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells, lymphocytes and eosinophils in lamina propria with thickened subepithelial collagen bands ( > 10 mm) | Chronic inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells, lymphocytes and eosinophils in the lamina propria with thickened subepithelia collagen bands (> 10 mm) |
| Treatment | -Spontaneous remission in some -Loperamide, sulfasalazine, bismuth, cholestyramine. -Budesonide/Corticosteroids -Azathioprine/Methotrexate -Colectomy/ileostomy | -Gluten free diet -Corticosteroids -Azathioprine/Methotrexate -Total parenteral nutrition -Intestinal transplant | -No definite therapy -Dietary modification -The following have been tried with varying results: sucralfate, ranitidine, mesalamine, elimination of gluten, loperamide, cholestyramine, budesonide and prednisione |
| Complications | Colonic fractures after endoscopic instrumentation, colonic ulceration due to concomitant NSAID use. Evolution into Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease have been reported | Nutrient deficiencies and progressive weight loss due to malabsorption. T cell Lymphoma similar to as in Celiac disease, Ulcerative jejunitis have been reported | Anemia in children Rare: Upper GI bleed, perforating gastric ulcer, dysphagia due to Plummer Vinson syndrome reported in adults |
| Clinical Outcome | -Good | -Poor with only few cases reported to have complete resolution of symptoms | -Fair but mostly unknown |