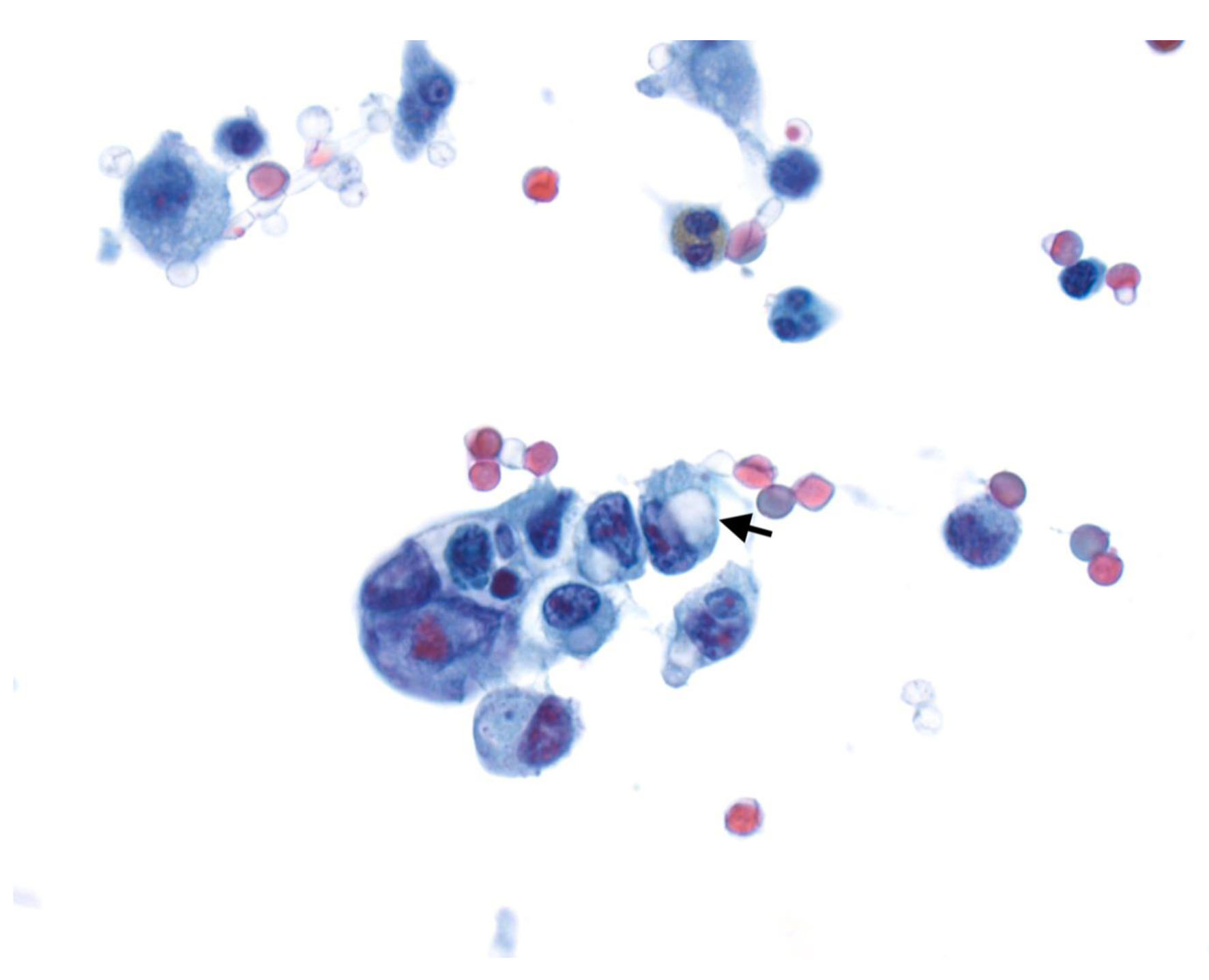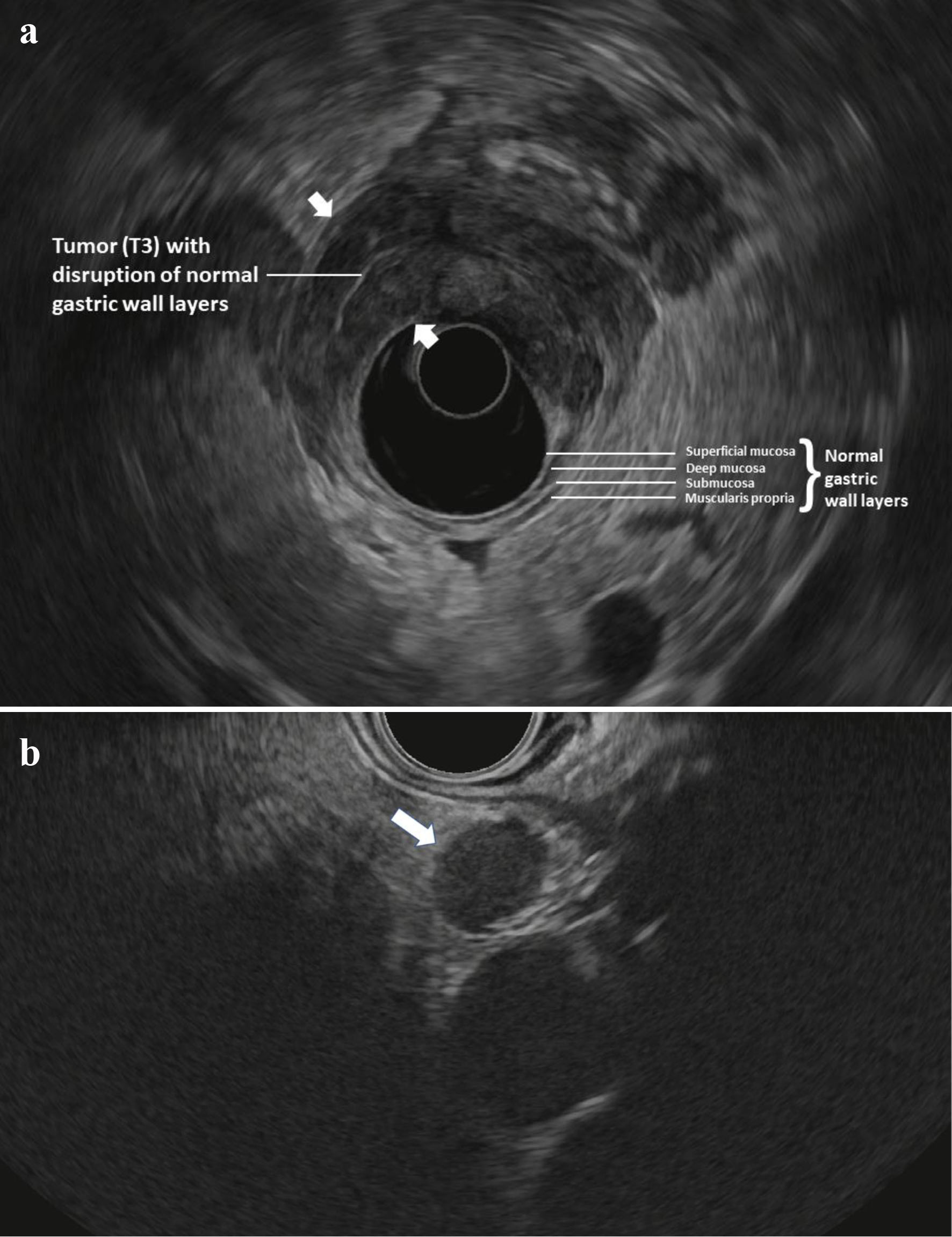
Figure 1. (a) Radial EUS image of a T3 antral tumor showing normal gastric layers on EUS and the large tumor (between arrowheads) disrupting the normal layers and invading through the muscularis propria and into the serosa. This patient was classified as “high-risk” and ultimately was found to have M1 disease on DSL. (b) Linear EUS image of an N+ tumor showing a malignant appearing lymph node (arrow). EUS: endoscopic ultrasound; DSL: diagnostic staging laparoscopy.