Figure 1. Literature review process.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 15, Number 1, February 2022, pages 26-32
Hemorrhagic Ascites Is Associated With Reduced Survival in Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
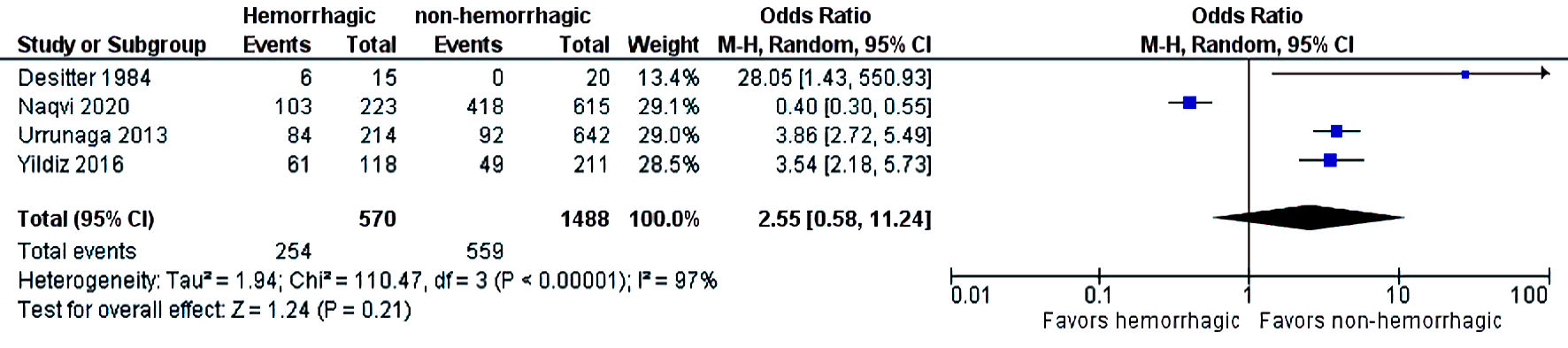
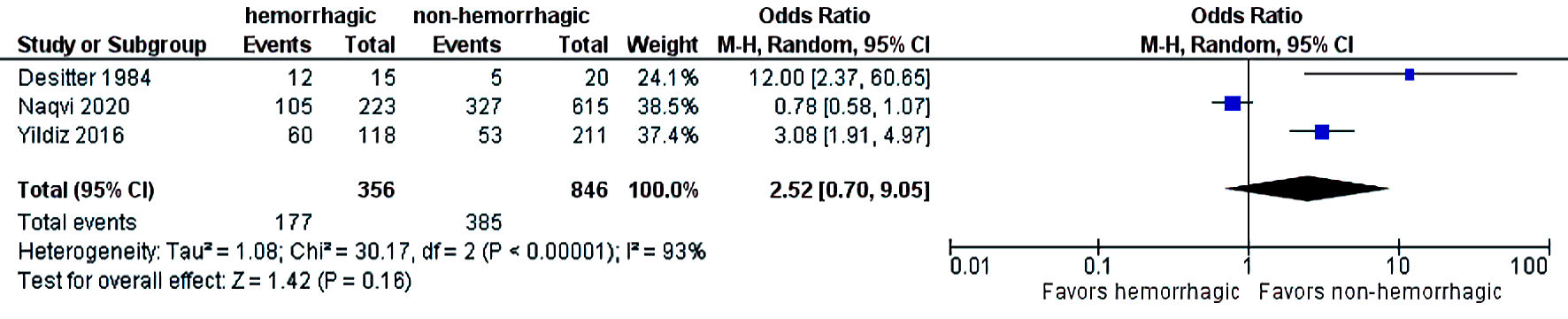
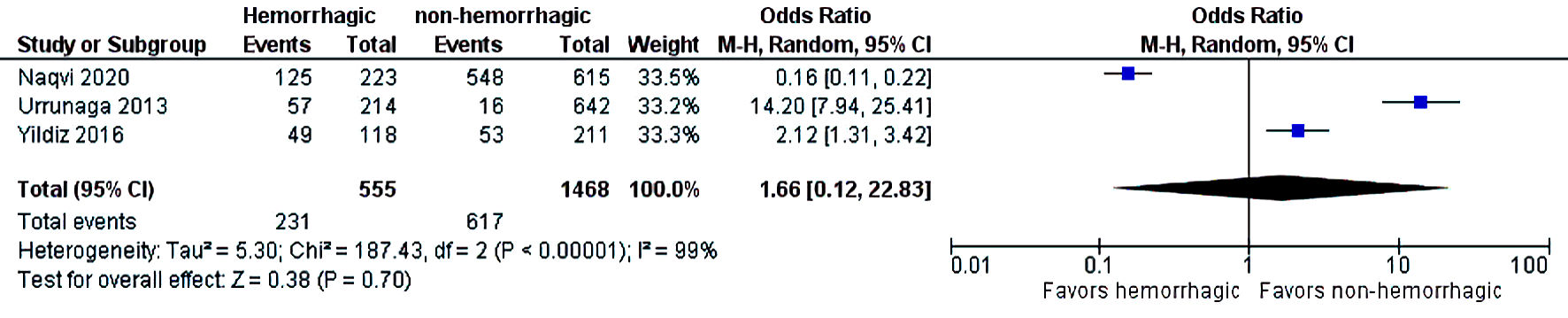
Figures

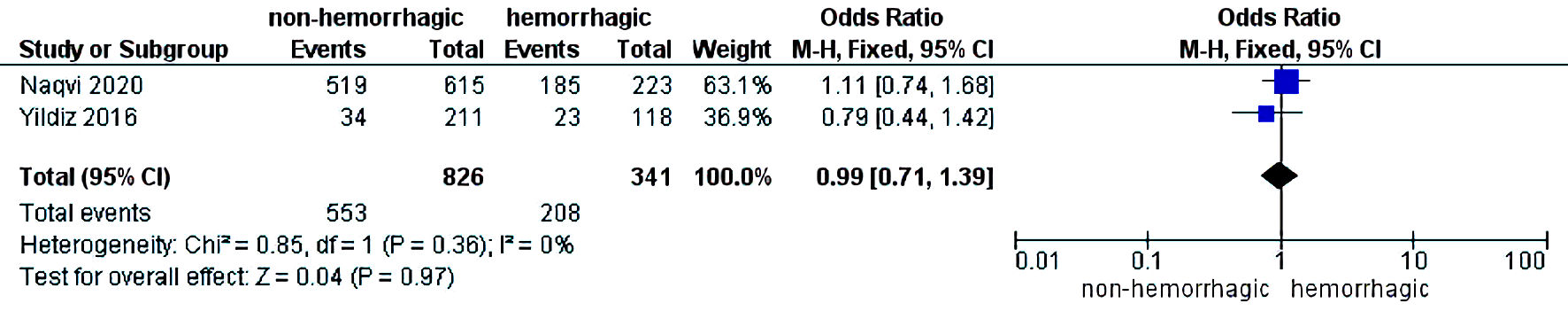
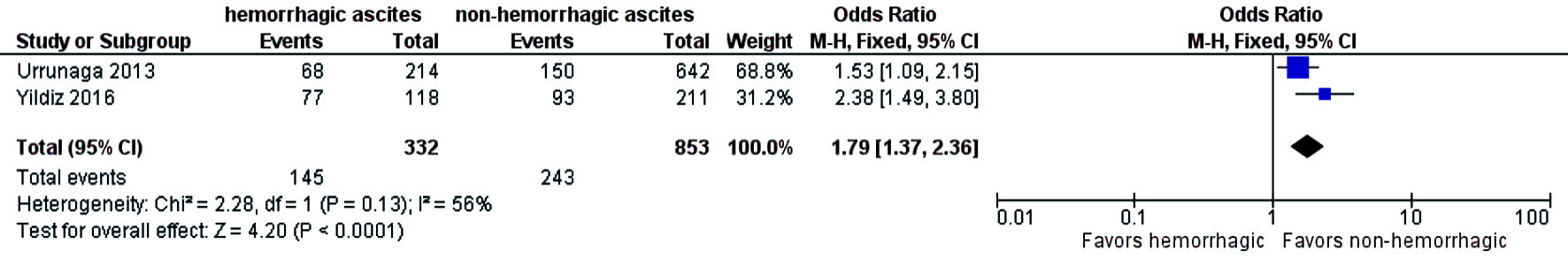
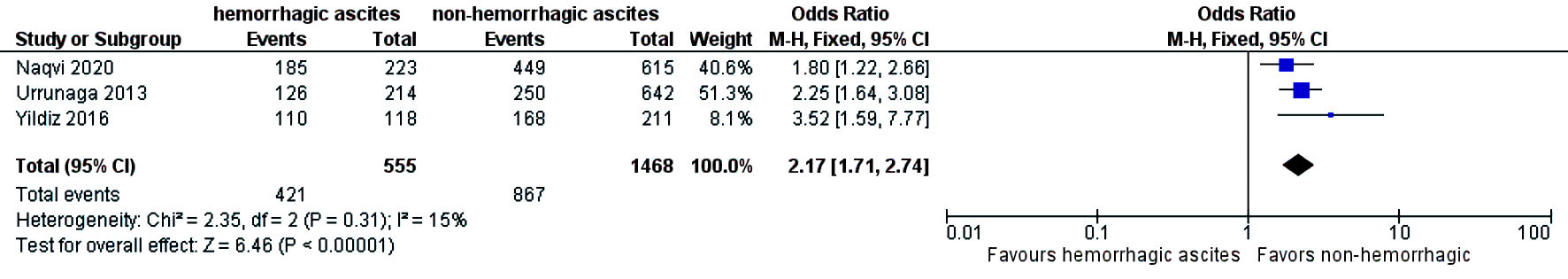
Table
| Study, year | Desitter et al, 1984 [13] | Urrunaga et al, 2013 [10] | Naqvi et al, 2020 [15] | Yildiz et al, 2016 [14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aComparative outcomes were reported in only 35 patients. NHA: non-hemorrhagic ascites; HA: hemorrhagic ascites; MELD; model for end-stage liver disease; N: total sample size; PT: prothrombin time; CTP: Child-Turcot-Pugh score; INR: international normalized ratio. | ||||
| Sample size, n | 800a | 856 | 838 | 329 |
| HA | 39 | 214 | 223 | 118 |
| NHA | 761 | 642 | 615 | 211 |
| Study design | Retrospective, observational study | Retrospective, observational study | Retrospective, observational study | Retrospective, observational study |
| Baseline demographics | ||||
| HA | ||||
| Mean age: 47 ± 11 | Median age: 51 (24 - 77) | Median age: 44.8 ± 14.5 | Mean age: 58.3 ± 14.4 | |
| PT: 39 ± 20 | Gender: females 22% | Gender: male 61% | Gender: females 44% | |
| Median MELD: 18 (6 - 46) | Mean MELD: 23.1 ± 9 | Mean MELD: 21.5 ± 8.3 | ||
| INR: 1.5 (0.9 - 5.8) | INR: 1.8 ± 0.4 | INR: 1.7 ± 0.6 | ||
| Platelets: 101 (11 - 660) | Platelets: 121 ± 29 | Platelets: 108 ± 63.7 | ||
| Mean CTP: 10 ± 1.7 | Mean CTP: 10.4 ± 2.1 | |||
| NHA | ||||
| Mean age: 43 ± 12 | Median age: 51 (22 - 79) | Mean age: 49 ± 13.4 | Mean age: 59.1 ± 12.8 | |
| PT: 35 ± 20 | Gender: females 22% | Gender: male 62% | Gender: females 75% | |
| Median MELD: 16 (6 - 46) | Mean MELD: 19.2 ± 6 | Mean MELD: 17.3 ± 6.6 | ||
| INR: 1.4 (0.9 - 6.1) | INR: 1.5 ± 0.3 | INR: 1.6 ± 0.4 | ||
| Platelets: 112.5 (9 - 2,631) | Platelets: 127 ± 49 | Platelets: 110 ± 91 | ||
| Mean CTP: 9.1 ± 1 | Mean CTP: 9.8 ± 2.2 | |||
| Etiology of cirrhosis | ||||
| HA | ||||
| Alcoholic liver disease 95% | Hepatitis C 52%, alcohol 33%, hepatitis B 4%, others 11% | Hepatitis C 61%, hepatitis B 26%, Wilson disease 4%, hemochromatosis 1% | Hepatitis B 38%, hepatitis C 11.2%, alcohol 7.8%, autoimmune 14.7%, others 28.4% | |
| NHA | ||||
| Alcoholic liver disease 87% | Hepatitis C 50%, alcohol 38%, hepatitis B 4%, others 8% | Hepatitis C 61%, hepatitis B 26%, Wilson disease 4%, hemochromatosis 1% | Hepatitis B 37.6%, hepatitis C 13.8%, alcohol 6.2%, autoimmune 15.7%, others 26.7% | |
| Cause of HA | Spontaneous 33-51% (charts of seven patients could not be retrieved), hepatocellular carcinoma 28%, traumatic 18%, tuberculous peritonitis 2.6% | Spontaneous 64.4%, hepatocellular carcinoma 17%, iatrogenic 13%, others 4.6 %, trauma 1% | Spontaneous 79%, hepatocellular carcinoma 14%, iatrogenic 7.6% | Spontaneous 82.3%, hepatocellular carcinoma 15.1%, iatrogenic 2.5% |
| Quality assessment | Fair | Good | Good | Good |