Figures
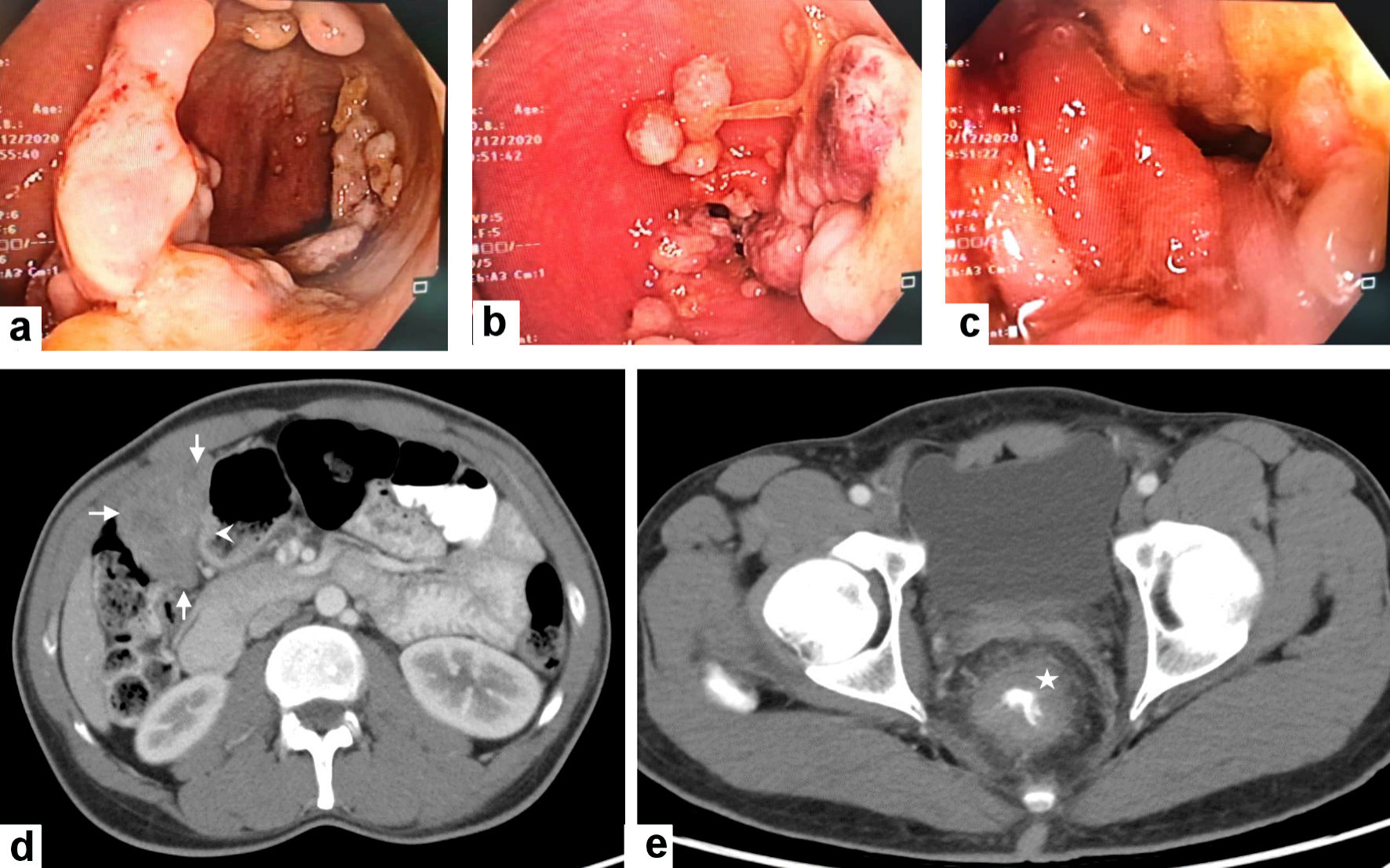
Figure 1. Colonoscopic and radiological features of the gastric GIST and rectal adenocarcinoma. (a, b, c) Colonoscopy revealed the presence of a circumferential ugly-looking rectal fungating mass. (d) Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan of the abdomen reveals a large exophytic enhancing mass arising (arrows) from gastric pylorus (arrowhead) likely GIST. (e) CECT scan through the pelvis shows a circumferential wall thickening of the low rectum (asterisk). GIST: gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
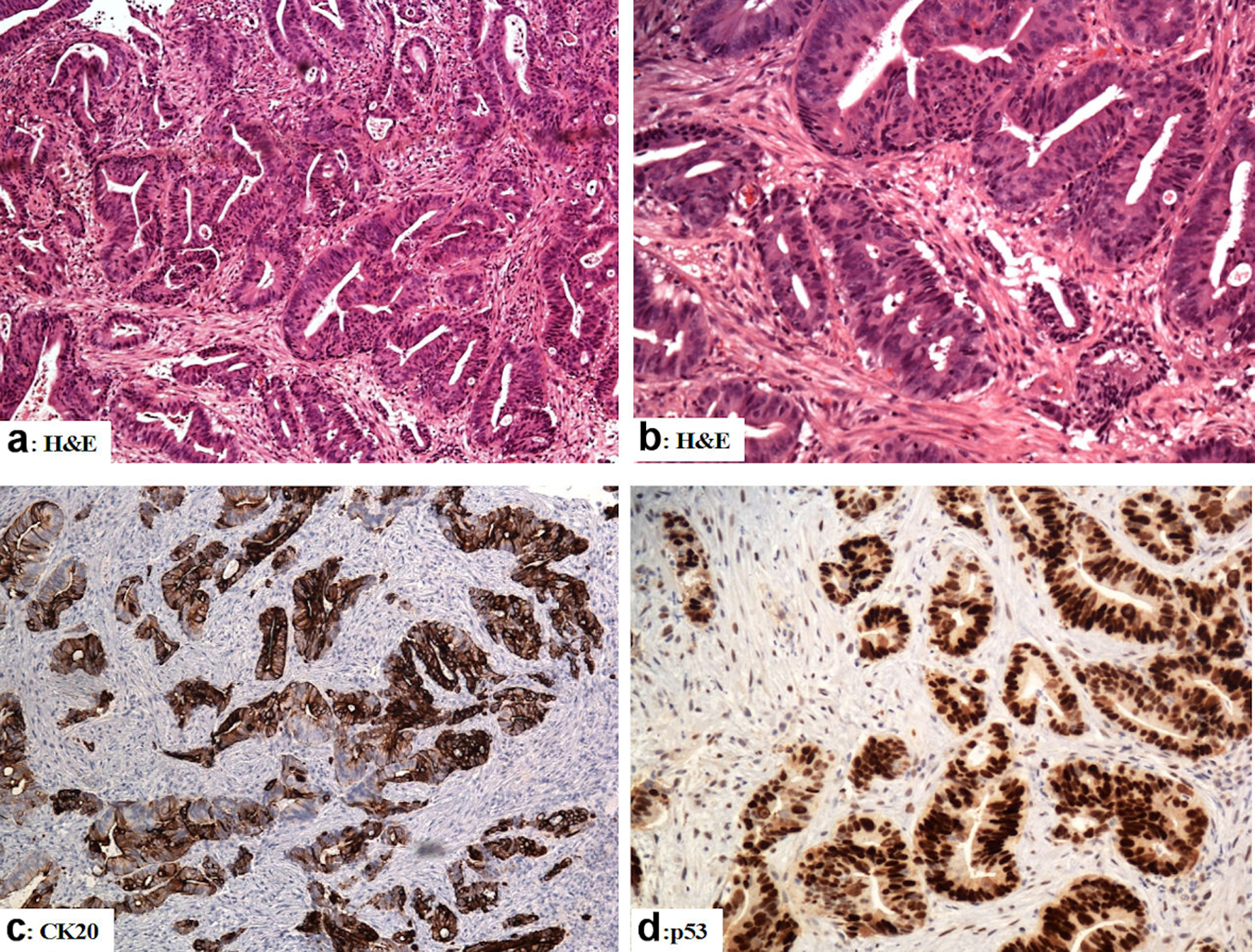
Figure 2. The immunohistological features of the rectal adenocarcinoma (colonoscopic biopsies). (a, b) Sections from the rectal mass show malignant glands with a complicated glandular pattern haphazardly scattered amid the desmoplastic stroma (H&E). (c) The tumor cells are reactive for CK20. (d) Mutation-type p53 diffuse strong reactivity in the tumor cells. Original magnifications: (a) × 100, (b) × 200, (c) ×100, (d) × 200. H&E: hematoxylin and eosin stain; CK: cytokeratin.
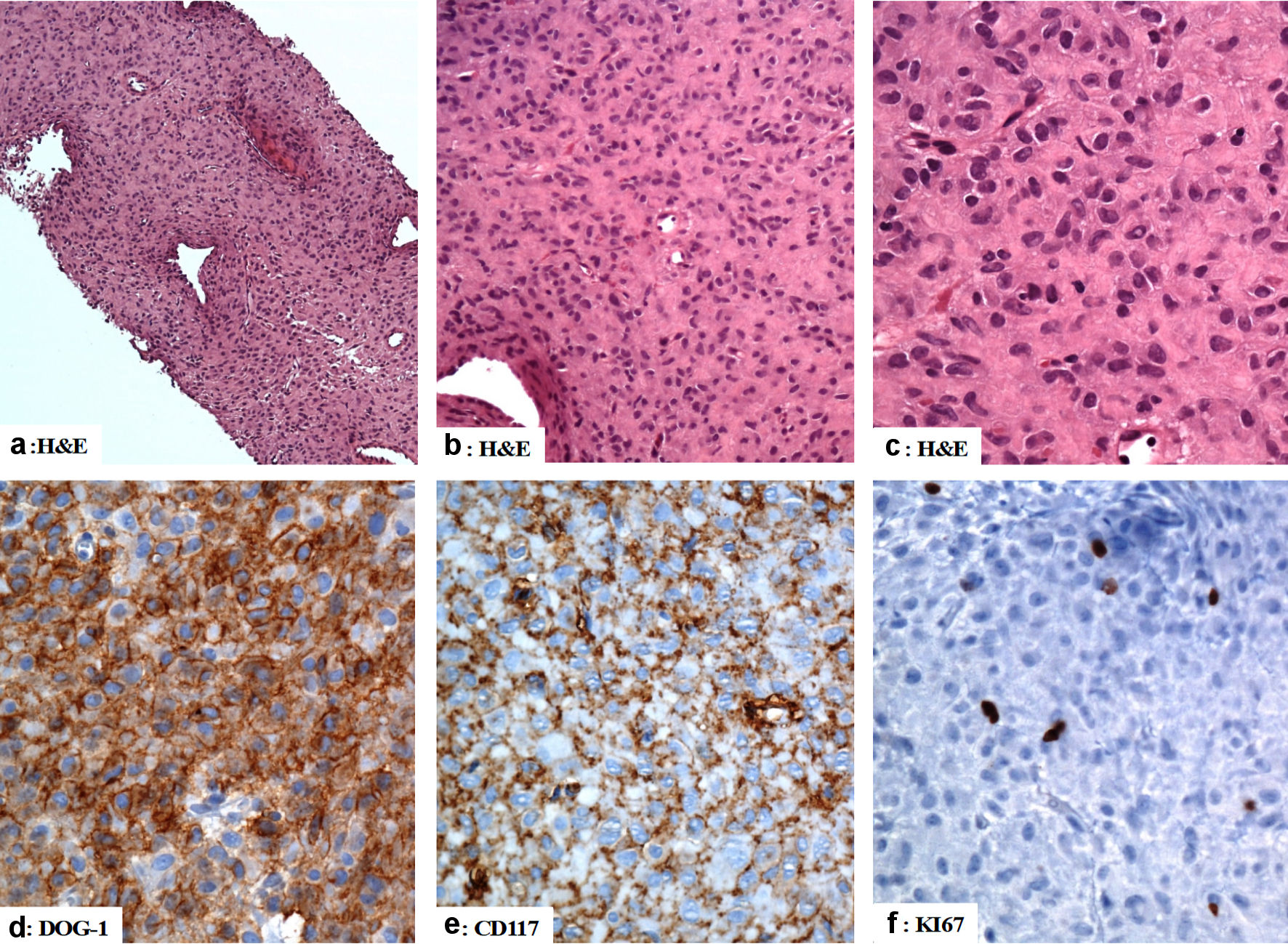
Figure 3. The immunohistological features of the gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor (computed tomography (CT)-guided biopsies). (a, b, c) The tumor is composed of mildly pleomorphic atypical spindle and epithelioid-shaped cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in a solid pattern. (d, e) The tumor cells are positive for DOG-1, and CD117. (f) The Ki67 labeling index is low. Original magnifications: (a) × 40, (b) × 200, (c) × 400, (d) × 400, (e) × 400, and (f) × 400. H&E: hematoxylin and eosin stain; CD: cluster of differentiation.
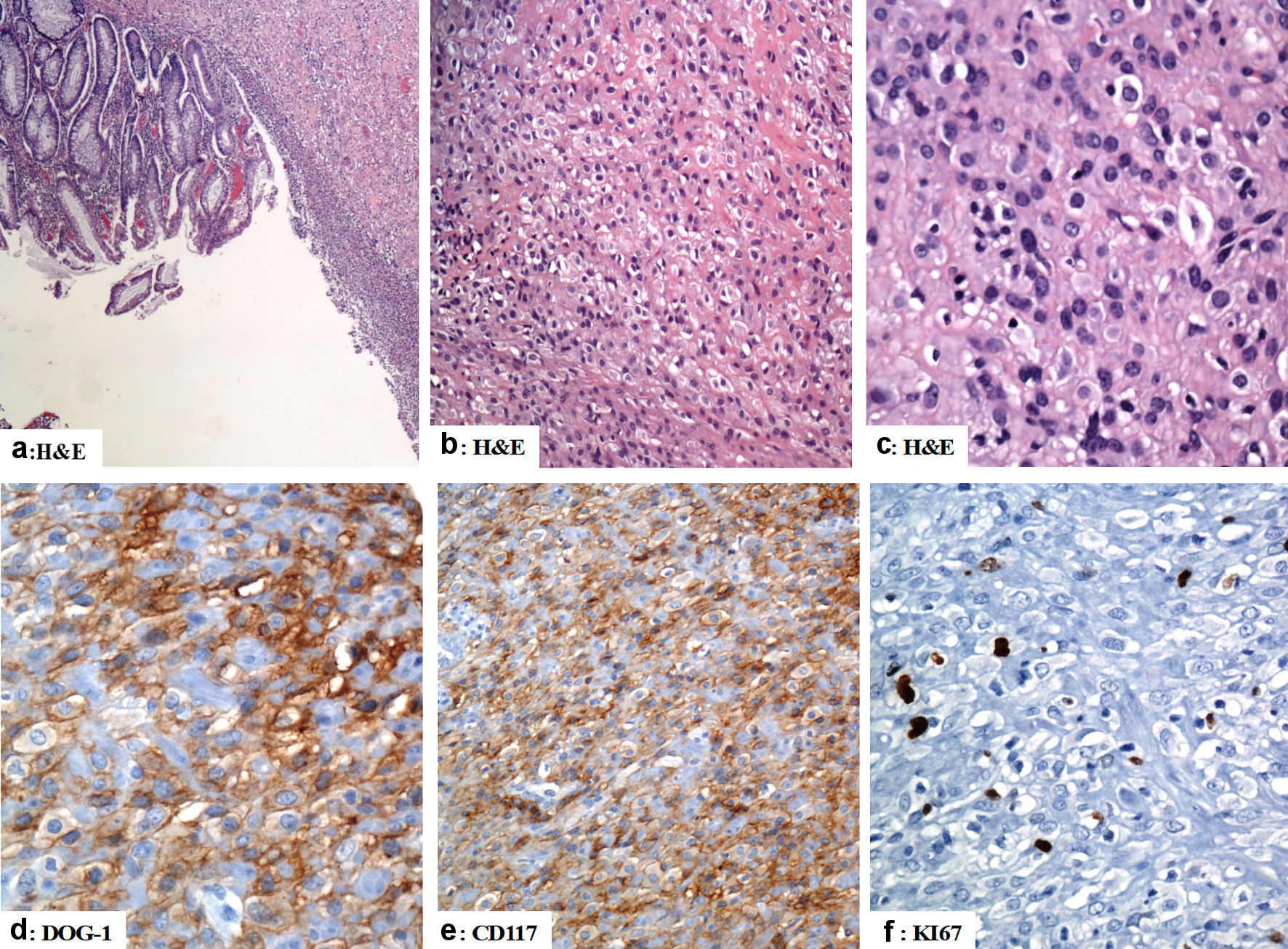
Figure 4. The immunohistological features of the gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor (excision of the gastric GIST). (a) There is focal ulceration of the mucosa with subepithelial neoplastic cells arranged in sheets. (b, c) The tumor cells have epithelioid morphology with vesicular nuclei and pink cytoplasm. (d, e) The tumor cells are positive for DOG-1 and CD117 (d and e, respectively). (f) Ki67 labeling index is low (less than 5%). Original magnifications: (a) × 40, (b) × 200, (c) × 400, (d) × 400, (e) × 200 and (f) × 400. H&E: hematoxylin and eosin stain; CD: cluster of differentiation.
Table
Table 1. Summary of the Previous Studies About Synchronous Colorectal Carcinoma and Other Malignant Neoplasms
| Studies | Age (years) | Sex | Site | References |
|---|
| GIST: gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor. |
| 1 | 76 | Male | Rectal adenocarcinoma | [21] |
| | | Prostatic carcinoma | |
| 2 | 70 | Female | Rectal carcinoma | [22] |
| | | Neurofibromatosis-1 | |
| | | Duodenal GIST | |
| 3 | 83 | Female | Rectal adenocarcinoma | [23] |
| | | Gastric GIST | |
| 4 | 63 | Female | Colonic carcinoma | [24] |
| | | Mammary cancer | |
| | | Colonic GIST | |
| 5 | 59 | Male | Sigmoid colon carcinoma | [25] |
| | | Gastric GIST | |
| 6 | 67 | Male | Lung small cell carcinoma | [26] |
| | | Rectal adenocarcinoma | |
| | | Jejunal GIST | |
| 7 | 72 | Male | Gastric adenocarcinoma | [27] |
| | | Gastric GIST | |



