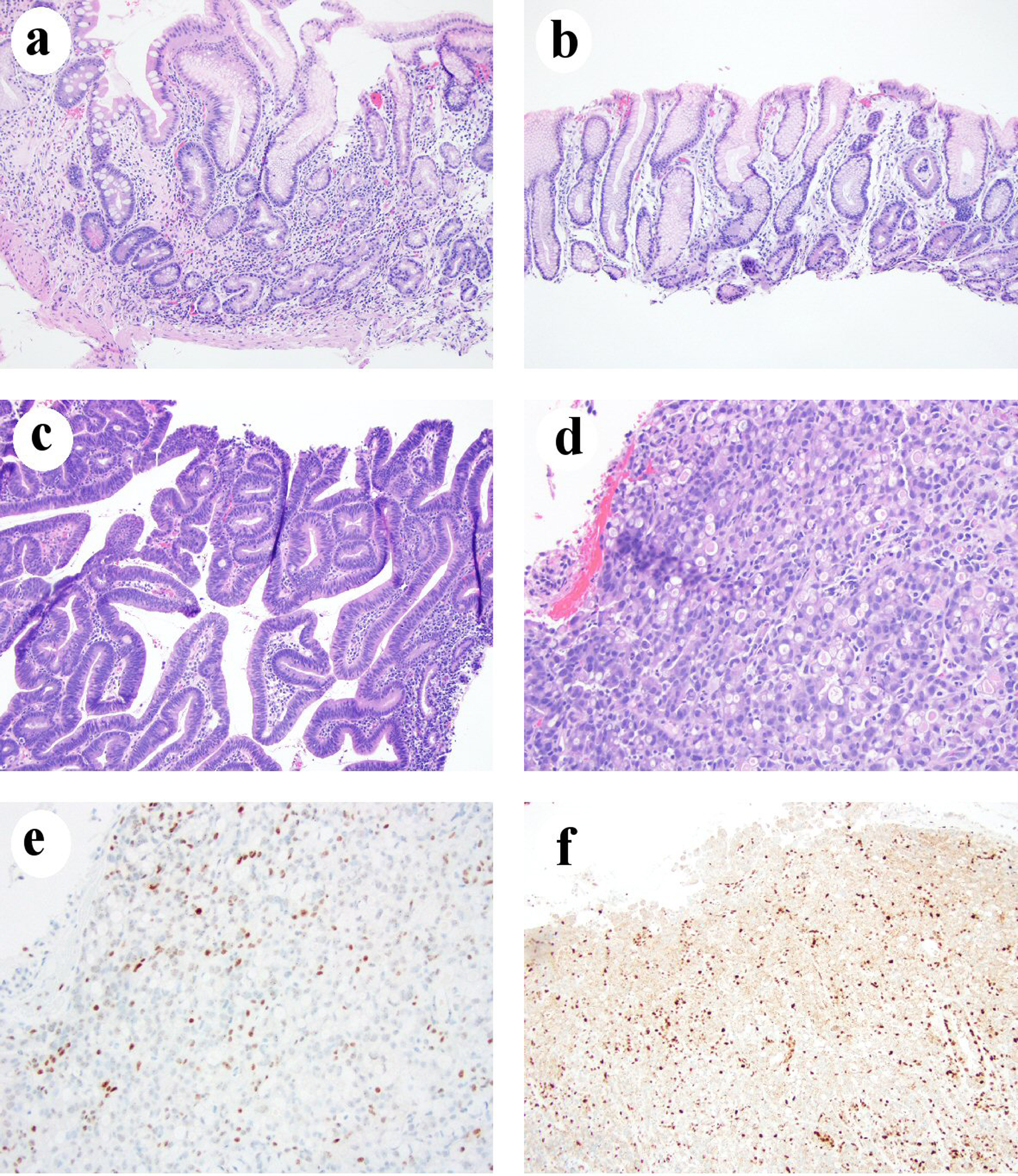
Figure 1. Chronic gastritis in one LS patient who developed gastric adenocarcinoma. (a) Body mucosa showing chronic inactive atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia and pseudopyloric gland metaplasia (H&E stain, 100 ×). (b) Antral mucosa showing mild chronic inactive gastritis without intestinal metaplasia (H&E stain, 100 ×). (c) Histomorphology of low-grade dysplasia (H&E stain, 100 ×). (d) Signet ring cell/diffuse type carcinoma (H&E stain, 200 ×). (e) Loss of MLH1 in gastric adenocarcinoma nuclei (immunohistochemical stain, 200 ×). (f) Loss of PMS2 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma nuclei (immunohistochemical stain, 100 ×). H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; LS: Lynch syndrome.