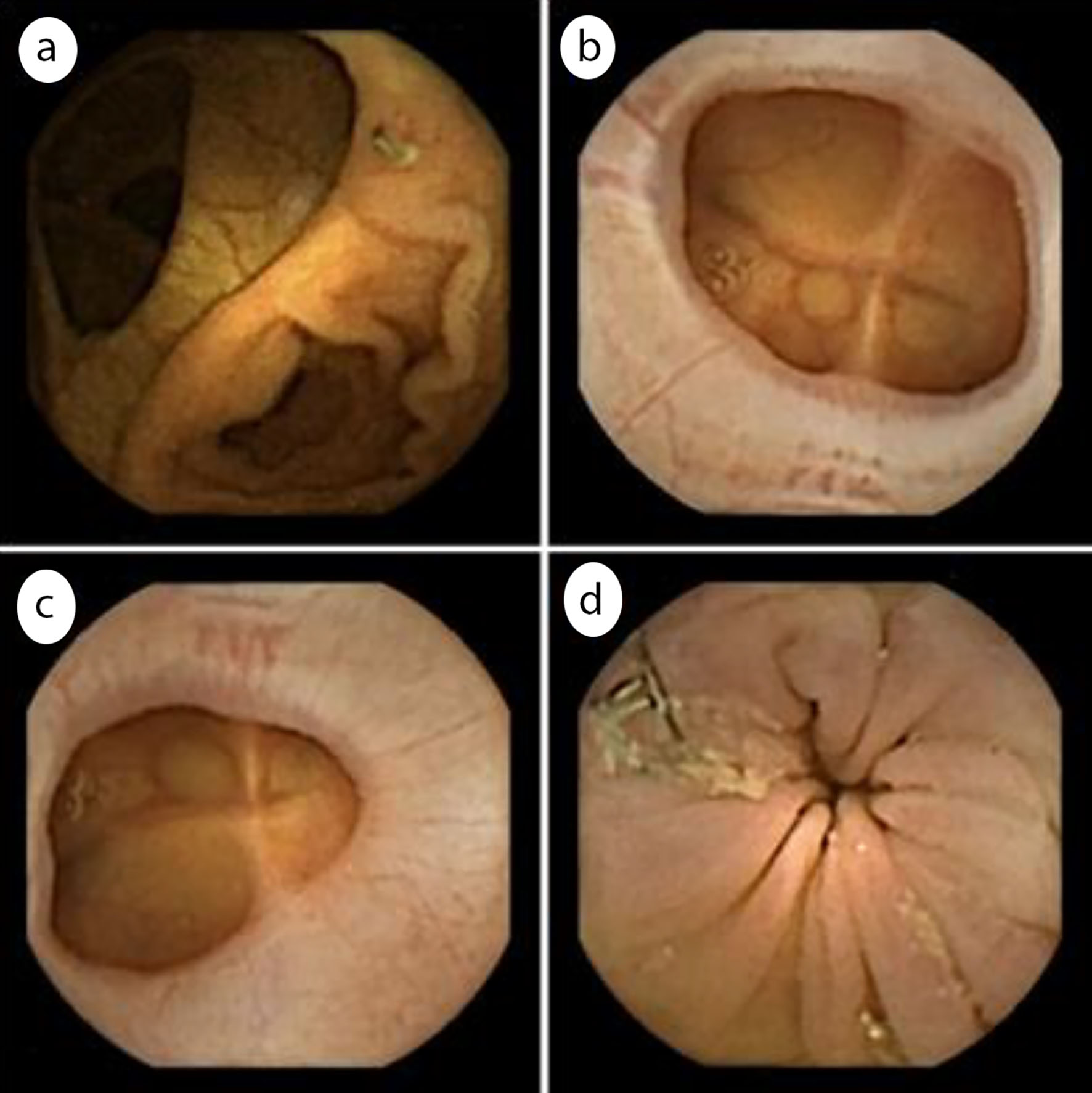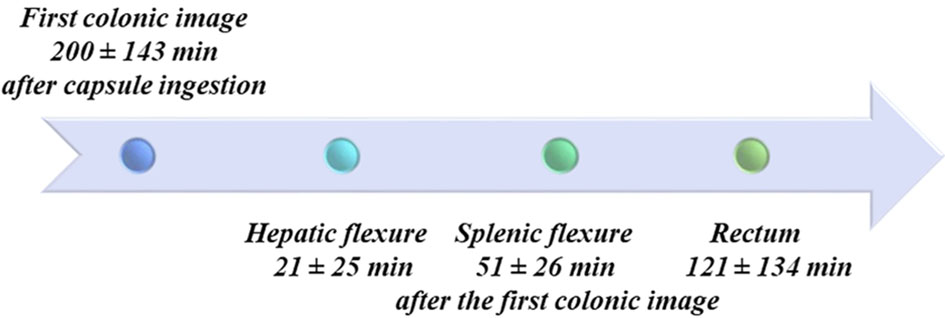
Figure 1. Colonic acquisitions timeline. Anatomical landmarks used to assess the progression of the capsule along the colon are shown with times of capsule passage. In some cases, landmarks were difficult to recognize due to alterations of the colonic lumen by the surgical resection and anastomosis, which is why these data were not analysed further.