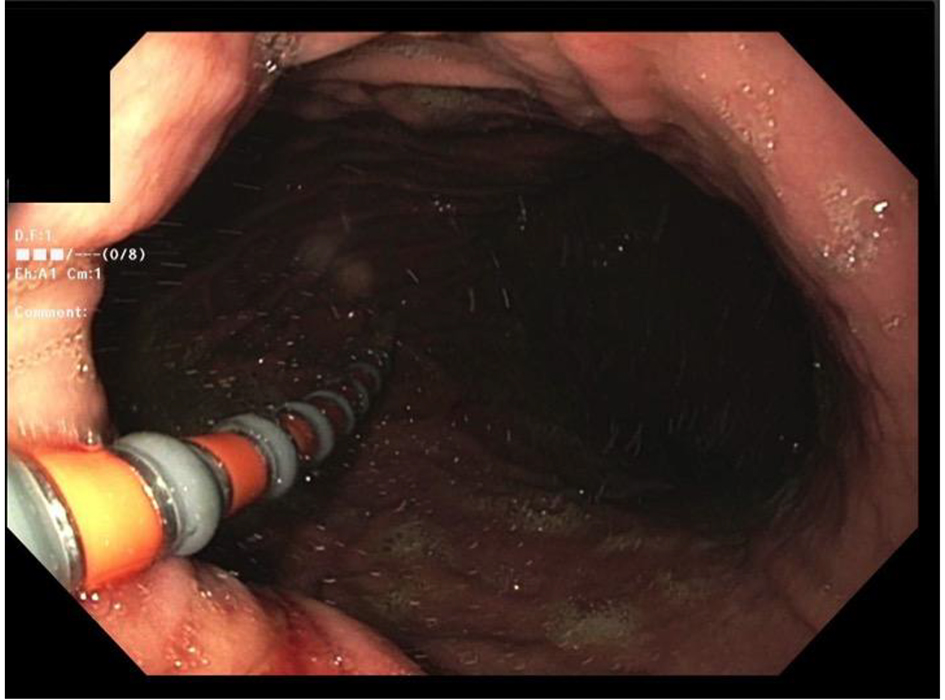
Figure 1. The passage of the catheter across esophagogastric junction (EGJ).
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 12, Number 3, June 2019, pages 157-165
Revisiting the Reliability of the Endoscopy and Sedation-Assisted High-Resolution Esophageal Motility Assessment
Figures

Tables
| Case no. | Age | Gender | Indication for HRM | Indication for endoscopy assistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRM: high-resolution manometry; EGJ: esophagogastric junction. | ||||
| 1 | 81 | Female | Dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse EGJ and coiling of catheter |
| 2 | 63 | Male | Dysphagia evaluation | Patient discomfort and coiling of the catheter |
| 3 | 57 | Female | Dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse EGJ and coiling of catheter |
| 4 | 57 | Male | Dysphagia evaluation | Patient discomfort and pharyngeal catheter coiling |
| 5 | 63 | Male | Dysphagia evaluation | Patient discomfort |
| 6 | 54 | Male | Pre-operative evaluation of type 3 para-esophageal hiatal hernia repair and fundoplication | Coiling of the catheter in the distal esophageal diverticulum and hernia sac |
| 7 | 50 | Male | Pre-operative evaluation of type 1 para-esophageal hiatal hernia repair and fundoplication | Large hiatal hernia and coiling of catheter in hernia |
| 8 | 74 | Male | Dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse EGJ and coiling of catheter |
| 9 | 66 | Female | Dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse EGJ and coiling of catheter |
| 10 | 66 | Female | Dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse EGJ and coiling of catheter |
| 11 | 58 | Female | Fundoplication revision pre-operative evaluation | Patient discomfort and inability to traverse EGJ |
| 12 | 51 | Male | Dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse EGJ and coiling of catheter |
| 13 | 49 | Female | Pre-operative evaluation of type 3 hiatal hernia repair and fundoplication | Large hiatal hernia and coiling of catheter in hernia |
| 14 | 61 | Female | Post-operative distal esophagectomy dysphagia evaluation | Inability to traverse the EGJ |
| Case no. | Diagnosis on HRM | IRP | DL | Esophageal peristalsis | Correction for IRP inflation (10%) | Barium esophagogram |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRM: high-resolution manometry; EGJ: esophagogastric junction; IRP: integrated relaxation pressure; DL: distal latency. | ||||||
| 1 | Type I achalasia | 22 | Aperistalsis | 20 | Not performed | |
| 2 | Type II achalasia | 24 | 2.1 | Isobaric pan-esophageal pressurization | 22 | Mildly diminished esophageal motility with dilatation |
| 3 | Type I achalasia | 22 | Aperistalsis | 20 | Achalasia pattern of the esophagus with narrowing above EGJ | |
| 4 | Type II achalasia | 36 | 2.4 | Isobaric pan-esophageal pressurization | 32 | Diminished motility with dilatation of the lower esophagus |
| 5 | Type II achalasia | 24 | 2.2 | Isobaric pan-esophageal pressurization | 22 | Dilatation of the lower esophagus |
| 6 | Ineffective esophageal motility | 14 | 5.2 | Ineffective esophageal motility | 13 | Not performed |
| 7 | Normal esophageal motility | 14 | 5.1 | Normal esophageal motility | 13 | Large hiatal hernia with reflux |
| 8 | Ineffective esophageal motility | 8 | 4.9 | Ineffective esophageal motility | 7 | Gastroesophageal reflux |
| 9 | EGJ obstruction | 20 | 5.1 | Normal esophageal motility | 18 | Small hiatal hernia |
| 10 | EGJ obstruction | 33 | 4.9 | Normal esophageal motility | 30 | No dilatation with poor emptying of esophagus |
| 11 | Normal esophageal motility | 14 | 5.1 | Normal esophageal motility | 13 | Mild degree of gastroesophageal reflux seen through the fundoplication |
| 12 | Type III achalasia | 30 | 2.1 | Simultaneous esophageal contraction | 27 | Incomplete emptying of the lower esophagus |
| 13 | Ineffective esophageal motility | 7 | Ineffective esophageal motility | 6 | Large hiatal hernia with reflux | |
| 14 | Normal esophageal motility | Not available due to surgical resection of the lower esophageal sphincter | Normal | Patent EGJ anastomosis | ||
| Case no. | Diagnosis on manometry | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| HRM: high-resolution manometry; EGJ: esophagogastric junction; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease. | ||
| 1 | Type I achalasia | Patient refused balloon dilatation and Heller’s myotomy - managed with calcium channel blocker |
| 2 | Type II achalasia | Heller’s myotomy |
| 3 | Type I achalasia | Balloon dilation, patient refused Heller’s myotomy |
| 4 | Type II achalasia | Patient refused balloon dilatation and Heller’s myotomy - managed with calcium channel blocker |
| 5 | Type II achalasia | Heller’s myotomy |
| 6 | Ineffective esophageal motility | Nissen’s fundoplication |
| 7 | Normal esophageal motility | Toupet’s 270° fundoplication |
| 8 | Ineffective esophageal motility | GERD management |
| 9 | EGJ obstruction | Observant management |
| 10 | EGJ obstruction | Observant management |
| 11 | Normal esophageal motility | Planned for the revision of the fundoplication |
| 12 | Type III achalasia | Heller’s myotomy |
| 13 | Ineffective esophageal motility | Undergoing evaluation for Nissen’s fundoplication |
| 14 | Normal esophageal motility | Dilatation of the esophago-gastric anastomosis |
| Case no. | HRM catheter calibration (min) | EGD duration (min) | Post-sedation recovery (min) | HRM acquisition (min) | Total procedure duration (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Catheter insertion with the sedation and no endoscopy. HRM: high-resolution manometry; EGD: esophagogastroduodenoscopy. | |||||
| 1 | 12 | 16 | 32 | 22 | 82 |
| 2 | 10 | 7 | 24 | 18 | 59 |
| 3 | 13 | 8 | 31 | 25 | 77 |
| 4 | 14 | 12 | 22 | 19 | 67 |
| 5 | 12 | 11 | 36 | 21 | 80 |
| 6 | 10 | 9 | 26 | 20 | 65 |
| 7 | 12 | 16 | 36 | 22 | 86 |
| 8 | 16 | 11 | 24 | 21 | 72 |
| 9 | 12 | 10 | 32 | 20 | 74 |
| 10 | 10 | 11 | 28 | 18 | 67 |
| 11 | 14 | 18 | 36 | 18 | 86 |
| 12 | 12 | 2* | 24 | 16 | 54 |
| 13 | 10 | 16 | 22 | 18 | 66 |
| 14 | 14 | 4* | 18 | 22 | 58 |
| Case no. | Propofol (mg) | Lidocaine (mg) | Metoprolol (mg) | Fentanyl (µg) | Midazolam (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 50 | |||
| 2 | 100 | 50 | 3 | ||
| 3 | 60 | 50 | |||
| 4 | 70 | 50 | 3 | ||
| 5 | 90 | 50 | 3 | ||
| 6 | 70 | 50 | 3 | ||
| 7 | 110 | 50 | 100 | ||
| 8 | 80 | 50 | 3 | ||
| 9 | 70 | 50 | |||
| 10 | 60 | 50 | 3 | ||
| 11 | 120 | 50 | 3 | 100 | |
| 12 | 40 | ||||
| 13 | 100 | 50 | |||
| 14 | 40 | 50 |